Barak Ravid in Axios reports that , “The Trump administration is closer to a major war in the Middle East than most Americans realize. It could begin very soon” in reference to Iran.
According to a source in the Trump administration, “it would likely be a joint U.S.-Israeli campaign that’s much broader in scope — and more existential for the regime — than the Israeli-led 12-day war last June.”
The report adds, “Trump’s armada has grown to include two aircraft carriers, a dozen warships, hundreds of fighter jets and multiple air defense systems. Some of that firepower is still on its way” adding, “The Israeli government — which is pushing for a maximalist scenario targeting regime change as well as Iran’s nuclear and missile programs — is preparing for a scenario of war within days, according to two Israeli officials.”
If this report is accurate, and the Trump administration actually is about to carry out a regime change war in Iran, there is only one driving motive behind it: the Zionist lobby’s control over Trump and broader U.S. foreign policy.
A Zionist Regime Change Campaign
During the June U.S./Israeli “12 day war”, Trump claimed it was about stopping Iran from obtaining Nuclear weapon, but Trump’s own Director of National Intelligence report from March found no evidence Iran was building a Nuclear weapon, writing, “We continue to assess Iran is not building a nuclear weapon and that Khamenei has not reauthorized the nuclear weapons program he suspended in 2003”.
The real motive behind the Israeli pushed war, was regime change in Iran.
An inside source in the Trump administration told journalists Max Blumenthal and Anya Parampil that Israeli intelligence officials who were pushing for U.S. involvement in the war “have demonstrated a single-minded focus on regime change, clamoring for authorization to assassinate Iran’s leader, Ayatollah Ali Khamenei. The Israeli officials have emphasized that the moment to take out Khamenei is now.”
The Times of Israel later reported on leaked transcripts of Israeli officials during the June bombing, which showed that the real motive was to “find an opportunity to assassinate Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei and destabilize Tehran’s regime”.
One senior Israeli intelligence official was quoted as saying that “for years” there was an Israeli “intelligence operation to disrupt enemy activities, including activity to destabilize the regime”.
The Times of Israel noted, “While not initially publicly stated as a goal of the war, the transcripts make it clear that Israel was also looking to destabilize the regime and even to kill Supreme Leader Ali Khamenei” adding, “Finance Minister Bezalel Smotrich said that Israel needed to ‘keep searching for the leader,’ referring to Khamenei” and “Netanyahu also said entire Iranian neighborhoods and districts should be evacuated, and that Israel should work on destabilizing the Islamic regime.”
Israel’s real motive behind the bombing, being regime change, is also underscored by the fact- uncovered by the University of Toronto’s Citizen Lab – that during the bombing, social media bots backed by Israeli intelligence ran a propaganda campaign “promoting regime change in Iran”. During the bombing, the Israeli bot network “published a series of posts highlighting the alleged economic upheaval in Iran after the first few rounds of bombings. The network told followers to head to ATMs to withdraw money, emphasized that the Islamic Republic was ‘stealing our money to escape with its officials,’ and urged followers to rise up against the regime,” and “urged followers to get on their balconies at 8 p.m. each evening and shout ‘Death to Khamenei’”.
In a later interview with the Daily Caller, Trump boasted that he took part in the bombing at the behest of Israel, boasting, “Israel is amazing, because, you know, I have good support from Israel. I have. Look, nobody has done more for Israel than I have, including the recent attacks with Iran”.
Following the “12-day war,” the U.S. and Israel exploited protests in Iran in an attempt to destabilize the Iranian government before the apparent upcoming regime change war.
After protests started in Iran due to citizens’ economic concerns, Trump’s Treasury Secretary Scott Bessent repeatedly boasted that the protests were the intended effect of U.S. sanctions on Iran designed to crash the Iranian economy, saying:
What we can do at treasury, and what we have done, is created a dollar shortage in the country, at a speech at the Economic club in New York in March I outlined the strategy, it came to a swift -and I would say grand- culmination in December when one of the largest banks in Iran went under, there was a run in the bank, the central bank had to print money, the Iranian currency went into free fall, inflation exploded and hence we have seen the Iranian people out on the street
and
If you look at a speech I gave at the economic club of New York last March, I said that I believe the Iranian currency was on the verge of collapse, that if I were an Iranain citizen, I would take my money out.
President Trump ordered treasury and our OFAC division, (Office of Foreign Asset Control) to put maximum pressure on Iran, and it’s worked because in December, their economy collapsed, we saw a major bank go under, the central bank has started to print money, there is a dollar shortage, they are not able to get imports and this is why the people took to the streets.
This is economic statecraft, no shots fired, and things are moving in a very positive way here
(Emphasis: Mine)
Similarly, the former Democratic Speaker of the House, Nancy Pelosi, boasted in response to the question, “Is there a way to bring about the (Iranian) regime falling without using American force?” : “Use economic force, there are ways that you can cripple their economy and some of that has been in the works. It’s more about just weaken their economy and it weakens the support they do have, because they do have support in the rural areas in the more conservative Imams and the rest of that, but we have to make them feel the pain as well”.
Following the protests sparked by economic sanctions on Iran, the Mossad and CIA infiltrated the protests to turn them into a pro-regime change direction.
A Mossad-connected social media account wrote in Persian, to Iranian protestors, “Come out to the streets together. The time has come. We are with you. Not only remotely and verbally. We are also with you in the field,” while former U.S. Secretary of State Mike Pompeo wrote , “Happy New Year to every Iranian in the streets. Also to every Mossad agent walking beside them.”
Israel’s Channel 14 similarly reported that, “foreign actors are arming the protesters in Iran with live firearms, which is the reason for the hundreds of regime personnel killed” while Israel’s Heritage Minister Amichai Eliyahu said , “When we attacked in Iran during ‘Rising Lion’ we were on its soil and knew how to lay the groundwork for a strike. I can assure you that we have some of our people operating there right now”.
Afterwards, the mainstream media ran a propaganda campaign claiming that Iran had killed tens of thousands of Iranian protestors, citing anonymous sources and explicitly pro-war and pro-regime change sources, including the German-Iranian eye surgeon Amir Parasta – a lobbyist for the Israeli puppet Reza Pahlavi – and Iran International, an outlet which journalist Barak Ravid said , “the Mossad is using… quite regularly for its information war”.
Given the likelihood of a U.S./Israeli regime change war happening, the propaganda campaign can be seen in the context of previous “atrocity propaganda” campaigns used to justify war such as the false claims that Saddam Hussein was throwing babies out of incubators in Kuwait used to justify the first Iraq war, false claims that Muammar Gaddafi was killing civilians in Libya used to justify the 2011 regime change war, and false claims that Hamas committed mas rape and beheaded babies on October 7th used to justify the genocide in Gaza.
Trump Controlled By The Zionist Lobby
If Trump launches a regime change war in Iran, his main motivating factor is the Zionist lobby’s influence over him.
While Trump began diplomatic talks with Iran in Oman, Benjamin Netanyahu flew to Washington to pressure Trump to make unrealistic demands, including demanding Iran give up its ballistic missiles, in order to sabotage diplomacy and force a U.S. war on Iran.
As journalist Glenn Greenwald noted , “Israel is demanding that the U.S. go to war with Iran even if Tehran satisfies Trump’s demands on its nuclear program. Netanyahu is insisting that Trump also require Iran to give up its ballistic missiles before any deal can be signed: something no country would ever do.”
Given Trump’s record, it is highly likely that he will follow the demands of the Zionist lobby and go to war with Iran on behalf of Israel.
Trump has repeatedly boasted that the Zionist lobby- more specifically, pro-Israel mega donor Miriam Adelson – controls his Middle East policy.
Trump boasted during his speech to the Israeli Knesset that Miriam Adelson -and during his first term her late husband Sheldon- were “responsible for so much” of his Middle East policy, adding, “I actually asked her (Miriam Adelson) once, so Miriam, I know you love Israel, what do you love more, the United States or Israel? She refused to answer, which might mean Israel.”
Trump boasted that at the behest of the Adelsons, he “terminated the disastrous Iran nuclear deal”, “authorized the spending of billions of dollars which went to Israel’s defense” and “officially recognized the capital of Israel and moved the American Embassy to Jerusalem”.
Trump later boasted that , “Miriam (Adelson) gave my campaign $250 million” adding that during his first term in office, “her husband Sheldon was an amazing guy, he’d come up to the office, and there was nobody more aggressive than Sheldon … he would always say ten minutes it turned out to be an hour and a half and what he did was he fought for Israel, it’s all he really fought for”.
Along with Trump’s self-admitted capture by the Zionist lobby, there is even the possibility – given Trump’s connection to Jeffrey Epstein and the growing body of evidence that Epstein was an Israeli intelligence asset – that Israel will use sexual blackmail to get its way on Iran.
This was argued by former Israeli intelligence official Ari Ben-Menashe who said , “The Israeli’s are holding some of the sensitive stuff (in the Epstein files) and they might let it out when they feel threatened by Trump” adding, “I believe the Israelis have quite a bit of information that they can release that the Department of Justice doesn’t want to release” and adding that Israel is “very much against the talks with the U.S. and Iran”.
The Final Phase Of The ‘Clean Break’
An Israeli pushed American regime change war in Iran is nothing new, and is in reality the final phase of a long-term Zionist plot to “reshape the Middle East” in Israel’s favour, going back to the Iraq war.
As Columbia University’s Jeffrey Sachs explained:
In 1996, Netanyahu and his American advisors devised a ‘Clean Break’ strategy. They advocated that Israel would not withdraw from the Palestinian lands captured in the 1967 war in exchange for regional peace. Instead, Israel would reshape the Middle East to its liking. Crucially, the strategy envisioned the US as the main force to achieve these aims—waging wars in the region to dismantle governments opposed to Israel’s dominance over Palestine. The US was called upon to fight wars on Israel’s behalf.
The Clean Break strategy was effectively carried out by the US and Israel after 9/11. As NATO Supreme Commander General Wesley Clark revealed, soon after 9/11, the US planned to “attack and destroy the governments in seven countries in five years—starting with Iraq, then Syria, Lebanon, Libya, Somalia, Sudan, and Iran.”
The first of the wars, in early 2003, was to topple the Iraqi government. Plans for further wars were delayed as the US became mired in Iraq. Still, the US supported Sudan’s split in 2005, Israel’s invasion of Lebanon in 2006, and Ethiopia’s incursion into Somalia that same year. In 2011, the Obama administration launched CIA operation Timber Sycamore against Syria and, with the UK and France, overthrew Libya’s government through a 2011 bombing campaign. Today, these countries lie in ruins, and many are now embroiled in civil wars.
Netanyahu was a cheerleader of these wars of choice–either in public or behind the scenes–together with his neocon allies in the U.S. Government including Paul Wolfowitz, Douglas Feith, Victoria Nuland, Hillary Clinton, Joe Biden, Richard Perle, Elliott Abrams, and others.
Sachs documented that war with Iran in the final phase of this plan, noting:
In September 2023, Netanyahu presented at UN General Assembly a map of the ‘New Middle East’ completely erasing a Palestinian state. In September 2024, he elaborated on this plan by showing two maps: one part of the Middle East a “blessing,” and the other–including Lebanon, Syria, Iraq, and Iran–a curse, as he advocated regime change in the latter countries.
Israel’s war on Iran is the final move in a decades-old strategy. We are witnessing the culmination of decades of extremist Zionist manipulation of US foreign policy.
Lindsay Graham – one of Israel’s closest allies in the U.S. Senate outright admitted that the hope behind a U.S. regime change war in Iran is that it will cripple resistance in the Middle East to Israel and cause Arab States to normalize with Israel without a Palestinian State – paving the way for the “New Middle East” laid out by Netanyahu at the UN in 2023.
Graham boasted referring to regime change in Iran, “If we can pull this off, it would be the biggest change in the Mid East in a thousand years: Hamas, Hezbollah gone, the Houthis gone, the Iranian people an ally not an enemy, the Arab world moving towards Israel without fear, Saudi-Israel normalize, no more October the 7th”.
Graham’s comments mirror Netanyahu’s at the UN weeks before the start of the Gaza genocide.
As journalist Jeremy Scahill reported :
Just two weeks before the October 7 attacks, the Israeli leader delivered a speech at the UN General Assembly in New York, brandishing a map of what he promised could be the “New Middle East.” It depicted a state of Israel that stretched continuously from the Jordan River to the Mediterranean Sea. Gaza and the West Bank, as Palestinian lands, were erased.
During that speech, Netanyahu portrayed the full normalization of relations with Saudi Arabia as the linchpin of his vision for this “new” reality, one which would open the door to a “visionary corridor that will stretch across the Arabian Peninsula and Israel. It will connect India to Europe with maritime links, rail links, energy pipelines, fiber-optic cables.”
In 2024, Netanyahu held up another map at the UN portraying Iran and the axis of resistance as a “curse” in the way of this Israeli goal.
It is surely not a coincidence that Israel is hoping to resume the full-scale genocide in Gaza in a few months.
The Times Of Israel reported that , “Israel plans to afford Hamas a 60-day period to disarm, and if it does not, the Israeli military will go back to war in the Gaza Strip, a senior adviser to Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu said Monday.”
This is an obvious attempt to force the failure of ceasefire negotiations in Gaza to justify resuming the full scale genocide, given the fact, as journalist Jeremy Scahil reported , that, “Hamas will not accede to sweeping demands that the Palestinian resistance unilaterally disarm, nor will it submit to a total demilitarization of the Gaza Strip” adding, “the group is willing to negotiate on disarmament of resistance forces only if it is linked to a long-term ceasefire that restrains Israel and is accompanied by a political process that leads to the establishment of a Palestinian state and armed force capable of defending itself”.
Israel hopes that after a regime change war in Iran, it will be clear to carry out its ethnic cleansing plan in Gaza and the West Bank without opposition – and it wants to get the U.S. to carry out the operation on its behalf.
February 19, 2026
Posted by aletho |
Ethnic Cleansing, Racism, Zionism, Wars for Israel | Iran, Israel, Middle East, Palestine, United States, Zionism |
Comments Off on The Only Motive Behind The ‘Imminent’ U.S. War With Iran Is The Zionist Lobby
Ankara is telling the world that a selective and force-driven approach to the Iranian nuclear issue could ignite a chain reaction
In Ankara, the idea of Türkiye one day seeking a nuclear weapons option has never been entirely absent from strategic conversation. Yet in recent days it has acquired a sharper edge, as the region around Türkiye is sliding toward a logic in which raw deterrence begins to look like the only dependable language left.
Türkiye’s foreign policy has expanded far beyond the cautious, status-quo posture that once defined it. It has positioned itself as a mediator on Ukraine and Gaza, pursued hard security aims through sustained operations and influence in Syria, Iraq, and Libya, and inserted itself into competitive theaters from the Eastern Mediterranean to the Horn of Africa. President Recep Tayyip Erdogan has long framed this activism as a corrective to an international order he portrays as structurally unfair. His slogan that the world is bigger than five – referring to the UN Security Council – is a statement of grievance against a system in which a narrow group of powers retains permanent privileges, including an exclusive claim to ultimate military capability.
Within that narrative, nuclear inequality occupies a special place. Erdogan has repeatedly pointed to the double standards of the global nuclear order, arguing that some states are punished for ambiguity while others are insulated from scrutiny. His references to Israel are central here, because Israel’s assumed but undeclared nuclear status is widely treated as an open secret that does not trigger the same enforcement instincts as suspected proliferation elsewhere. That asymmetry has long irritated Ankara, but it became more politically potent after the war in Gaza that began in 2023, when Erdogan openly highlighted Israel’s arsenal and questioned why international inspection mechanisms do not apply in practice to all regional actors.
Still, for years this was mostly an argument about fairness and legitimacy rather than a declaration of intent. What has changed is the sense that the regional security architecture itself is cracking, and that the cracks are widening at the very moment the US and Israel are escalating pressure on Iran. Türkiye’s leadership has warned that if Iran crosses the nuclear threshold, others in the region will rush to follow, and Türkiye may be forced into the race as well, even if it does not want dramatic shifts in the balance.
This is the key to understanding the new intensity of the debate. Ankara’s signaling is not primarily an emotional reaction to Tehran. Türkiye and Iran remain competitors, but their frictions have also been managed through pragmatic diplomacy, and Türkiye has consistently argued against a military solution to the Iranian nuclear issue. Erdogan has again presented Türkiye as a mediator, insisting on de-escalation and rejecting military steps that could drag the region into wider chaos.
The driver is the fear that the rules are no longer the rules. When enforcement becomes selective, and when coercion is applied in ways that appear to disregard broader stability, the incentives change for every middle power caught in the blast radius. The signal from Ankara is that if the Middle East moves into a world where nuclear capability is treated as the only ironclad guarantee against regime-threatening force, then Türkiye cannot afford to remain the exception.
That logic is dangerous precisely because it is contagious. It turns proliferation into an insurance policy. In an unstable region where trust is thin and the memory of war is always fresh, the idea of nuclear weapons as a shield against interference can sound brutally rational. If possessing the bomb raises the cost of intervention to unacceptable levels, it can be perceived as the ultimate deterrent, a guarantee that outsiders will think twice. But the same logic that appears to promise safety for one actor produces insecurity for everyone else. In practice it fuels an arms race whose end state is not stability, but a crowded deterrence environment in which miscalculation becomes more likely, crisis management becomes harder, and conventional conflicts become more combustible because nuclear shadows hover over every escalation ladder.
The renewed urgency also reflects a broader global drift. Arms competition is intensifying well beyond the Middle East. The erosion of arms control habits, the normalization of sanctions as a tool of strategic coercion, and the return of bloc-like thinking in many theaters all contribute to a sense that restraint is no longer rewarded. For Türkiye, a state that sees itself as too large to be merely a client and too exposed to be fully autonomous, the temptation is to seek leverage that cannot be negotiated away. Nuclear latency, even without an actual bomb, can function as a strategic bargaining chip.
Yet the jump from ambition to capability is not straightforward. Türkiye does have important ingredients for a serious civil nuclear profile, and those capabilities matter because they shape perceptions. The country has been building human capital in nuclear engineering and developing an ecosystem of research institutions, reactors for training and experimentation, accelerator facilities, and nuclear medicine applications. Most visibly, the Akkuyu nuclear power plant project with Russia has served as an engine for training and institutional learning, even if technology transfer is limited and the project remains embedded in external dependence.
Türkiye also highlights domestic resource potential, including uranium and especially thorium, which is often discussed as a long-term strategic asset. Resource endowments do not automatically translate into weapons capability, but they reduce one barrier, the need for sustained and vulnerable supply chains. As a result, Türkiye can credibly present itself as a state that could, if it chose, move from peaceful nuclear competence toward a latent weapons posture.
The real bottleneck is not simply material. It is political and legal. Türkiye is a party to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty, and it operates inside a web of international commitments that would make an overt weapons program extremely costly. Withdrawal from the treaty or large-scale violations would almost certainly trigger sweeping sanctions, diplomatic isolation, and a rupture with major economic partners. Unlike states that have adapted their economies to long-term siege conditions, Türkiye is deeply integrated into global trade, finance, and logistics. The short-term shock of a proliferation crisis would be severe, and Ankara knows it.
This is why the most plausible path, if Türkiye ever moved in this direction, would not be a dramatic public sprint. It would be a careful, ambiguous strategy that expands latency while preserving diplomatic maneuvering room. Latency can mean investing in expertise, dual-use infrastructure, missile and space capabilities that could be adapted, and fuel cycle options that remain justifiable on civilian grounds. It can also mean cultivating external relationships that shorten timelines without leaving fingerprints.
Here the debate becomes even more sensitive, because proliferation risk is not only about what a country can build, but also about what it can receive. The Middle East has long been haunted by the possibility of clandestine technology transfer, whether through black markets, covert state support, or unofficial security arrangements. In recent months, discussions around Pakistan have become particularly salient, not least because Islamabad is one of the few Muslim majority nuclear powers and has historically maintained close security ties with Gulf monarchies.
Saudi Arabia has repeatedly signaled that it will not accept a regional balance in which Iran alone holds a nuclear weapon. Saudi leaders have at times implied that if Iran acquires the bomb, Riyadh would feel compelled to match it for reasons of security and balance. Those statements are not proof of an active weapons program, but they are political preparation, shaping expectations and normalizing the idea that proliferation could be framed as defensive rather than destabilizing.
There have also been unusually explicit hints in regional discourse about nuclear protection arrangements, including arguments that Pakistan could, in some scenario, extend a form of deterrence cover to Saudi Arabia. Even when such claims are partly performative, they underscore how the region’s strategic conversation is shifting from taboo to contingency planning.
Once that door is open, Türkiye inevitably enters the picture in regional imagination. Türkiye, Pakistan, and Saudi Arabia are linked through overlapping defense cooperation and political coordination, and analysts increasingly discuss the emergence of flexible security groupings that sit alongside or partially outside formal Western frameworks. The idea that technology, know-how, or deterrence guarantees could circulate within such networks is precisely the nightmare scenario for nonproliferation regimes, because it compresses timelines and reduces the visibility that international monitors depend on.
For Ankara, this creates both opportunity and risk. The opportunity is that Türkiye could enhance its deterrent posture without bearing the full cost of overt development. The risk is that Türkiye could become entangled in a proliferation cascade that it cannot control, while simultaneously inviting a Western backlash that would reshape its economy and alliances.
This is where the question becomes deeply geopolitical. A nuclear-armed Türkiye would not simply change the Middle East. It would alter Europe’s security landscape and challenge the logic that has governed Türkiye’s relationship with the West for decades. Western capitals have tolerated, managed, and constrained Türkiye through a mixture of incentives, institutional ties, defense cooperation, and pressure. Türkiye’s NATO membership, its economic links to Europe, and the presence of US nuclear weapons stored at Incirlik as part of alliance arrangements have all been elements of a broader strategic framework in which Türkiye was seen as anchored, even when politically difficult.
If Türkiye acquired its own nuclear weapons, that anchoring would weaken dramatically. Ankara would gain a form of autonomy that no sanction threat could fully erase. It would also gain the capacity to take risks under a nuclear umbrella, a dynamic that worries Western capitals because it could embolden more confrontational regional behavior. Türkiye’s disputes with Western partners are already intense on issues ranging from Eastern Mediterranean energy politics to Syria, defense procurement, and the boundaries of alliance solidarity. A nuclear deterrent could make those disputes harder to manage because the ultimate escalation dominance would no longer sit exclusively with the traditional nuclear powers.
At the same time, a Turkish bomb could accelerate Türkiye’s drift away from the West, not only because the West would react with pressure, but because the very act of building such a capability would be an ideological statement that Türkiye rejects a Western-defined hierarchy. It would be Ankara’s most dramatic way of saying that it will not accept a subordinate place in a system it considers hypocritical.
None of this means Türkiye is on the verge of producing a weapon. Political obstacles remain huge, and technical challenges would be substantial if Ankara had to do everything indigenously while under scrutiny. A credible weapons program requires enrichment or plutonium pathways, specialized engineering, reliable warhead design, rigorous testing regimes or sophisticated simulation capabilities, secure command and control, and delivery systems that can survive and penetrate. Türkiye has missile programs that could in theory be adapted, but turning a regional missile force into a robust nuclear delivery architecture is not trivial.
The more immediate danger is not that Türkiye will suddenly unveil a bomb, but that the region is moving toward a threshold era, in which multiple states cultivate the ability to become nuclear on short notice. In such an environment, crises become more perilous because leaders assume worst-case intentions, and because external powers may feel pressure to strike early rather than wait. The irony is that a weapon meant to prevent intervention can increase the likelihood of intervention if adversaries fear they are running out of time.
The escalation by the US and Israel against Iran, combined with the broader arms race logic spreading across the Middle East and globally, is making this spiral more plausible. Uncertainty is the fuel of proliferation, because it convinces states that the future will be more dangerous than the present, and that waiting is a strategic mistake.
Türkiye’s rhetoric should therefore be read as a warning as much as a threat. Ankara is telling the world that a selective and force-driven approach to the Iranian nuclear issue could ignite a chain reaction. It is also telling regional rivals that Türkiye will not accept a future in which it is strategically exposed in a neighborhood where others have ultimate insurance.
The tragedy is that this is exactly how nuclear orders unravel. They do not collapse when one state wakes up and decides to gamble. They collapse when multiple states simultaneously conclude that the existing rules no longer protect them, and that deterrence, however dangerous, is the only available substitute. In a stable region, that conclusion might be resisted. In the Middle East, where wars overlap, alliances shift, and trust is scarce, it can quickly become conventional wisdom.
If the goal is to prevent a regional nuclear cascade, the first requirement is to restore credibility to the idea that rules apply to everyone and that security can be achieved without crossing the nuclear threshold. That means lowering the temperature around Iran while also addressing the deeper asymmetries that make the system look illegitimate in the eyes of ambitious middle powers. Without that, Türkiye’s nuclear debate will not remain an abstract exercise. It will become part of a wider regional recalculation, one that risks turning an already unstable region into a nuclearized arena where every crisis carries the possibility of catastrophe.
Murad Sadygzade, President of the Middle East Studies Center, Visiting Lecturer, HSE University (Moscow).
February 18, 2026
Posted by aletho |
Ethnic Cleansing, Racism, Zionism, Militarism, Wars for Israel | Iran, Israel, Middle East, Saudi Arabia, Turkey, United States, Zionism |
Comments Off on Erdogan wants nukes: What a Turkish bomb would mean for the Middle East
Trump has the option of going to war with Iran and receiving much-needed campaign funds from Israel for the midterms – or opting to defy Bibi and facing certain defeat by losing both houses and facing certain impeachment. Can the Iranians save him?
Is Trump serious about going to war with Iran? To understand this, it’s important to examine his relationship with Netanyahu and to see who has the advantage when it comes to dragging the U.S. into a war, and whether Israel can actually be a greater threat to the U.S. than Tehran can ever be.
The trap that Trump is falling into is one where he has little or no wiggle room at all to control the Iran crisis, whereby Israel can threaten him with isolation while it goes ahead with its strike.
There are two dynamics at play here which are struggling to find a compromise. Trump wants a deal with Iran which takes away their nuclear capability, while Israel wants a war which overthrows the Iranian regime and installs a Mossad/CIA puppet. The problem, though, is that Israel is not an honest broker and keeps shifting the goalposts. The latest demand now is that removing Iran’s ballistic missiles should be at the heart of any deal that Trump pulls off.
Trump is ensnared and is aware of how Bibi is manipulating him. He may, on occasion, swear at journalists and pretend he is his own boss and his own president and that Israel is a client state of Washington which has to toe the line, but in reality, it is clear that Israel is calling the shots.
In recent days, we have heard that the one aircraft carrier the U.S. had in the region, the USS Abraham Lincoln, is to be joined by a second called the USS Gerald Ford. U.S. media report that the Lincoln is in the “Arabian Sea,” which is a comical way of saying that it’s keeping its distance from Iran’s shores and Houthi missiles off the coast of Yemen. But other reports are suggesting that the reason why Trump claims he has sent a second carrier – to beef up the “flotilla” in case of a war breaking out with Iran – is untrue. Some insiders are briefing journalists that the Lincoln has technical problems which will render it useless in a combat situation and so needs to be replaced with the more advanced Ford.
However, even this might be a false narrative offered by Pentagon insiders who are not supporters of Trump. A second explanation about the carriers is that it buys Trump time. He has even told reporters that it will take about a month for the Ford to get there, which he believes should be ample time for a deal to be struck with Iran, or at least will give him four more weeks to work out a way of dealing with the threat – that’s the threat from Israel, not Iran.
Israel threatened Trump before when he went ahead with his bunker buster bombs in June of last year by saying simply, “If you don’t do it, we’ll nuke Iran.” It worked. This time around, the threat is, “If you don’t join us, then we’ll strike Iran alone and you will have to deal with the consequences of being the first U.S. president to have to explain to the Jewish lobby why Iran is wiping Israel off the face of the map.” This second threat is multi-layered and also might work with Trump, given that the midterm elections, which are approaching, will cost twice what the elections cost which got him into office. It will be Jewish money which bankrolls him this time around, with the intention of saving him from losing both houses and facing inevitable impeachment.
And so, in many ways, Trump is closer to and more dependent on the regime in Tehran to help him out. A deal which limits the enrichment of uranium and can guarantee no nuclear bomb can be made might be something he can present to the American people as a great victory. The irony is that the deal might be more or less a carbon copy of Obama’s, which he, Trump, rejected while in his first term in office, a rejection which has created the present crisis.
The trouble with any deal now about enrichment is that it is unlikely to satisfy the Israelis, who have become more aware in recent weeks about the capability of Iran’s latest generation of ballistic missiles both in terms of defence and attack. Moreover, the U.S. attack on Iran last year for 12 days has now raised the stakes to a fever pitch, making the Iranians clearer and more focused about any kind of attack happening against them: all-out war.
According to some credible reports, Trump was recently asking Pentagon chiefs if the U.S. could carry out a single in-and-out strike operation which could be used to warn Iran while satisfying Israel at the same time about the U.S. threat, and he was told no such options are feasible. This is due to Iran being much more prepared now for such attacks, both militarily and intelligence-wise, while the Mossad operation of creating civil strife on the ground failed spectacularly. The U.S. is in a very tight corner right now, as its forces and its allies in the region are in the crosshairs of Iran the moment the first bomb is dropped, and so Trump’s options to go to war are very limited. It would be suicidal for Trump to strike Iran, as the losses to U.S. forces and the disruption to oil distribution via the Straits of Hormuz would be too great, not to mention the destruction of infrastructure in Israel itself.
But there is also another factor which is putting all the pressure on Trump to get a deal with Iran. Since last June’s attack and more recently Trump’s betrayal of cordial relations with Putin conjured up at Alaska, along with the Venezuela coup, both Russia and China have upped their support for Iran. This is a critical factor now preventing Trump from hitting Iran with anything. China recently gave Iran its latest state-of-the-art new radar system which can identify U.S. stealth bombers at a range of 700km. Game changer. If you consider Iran, Israel, and the U.S. as three poker players at the table, it is clear that Iran now has the best hand with the most options. It can maximize its role now and exploit Trump’s vulnerability by going for a deal which involves sanctions being relieved, or it could hold out and play a long game way beyond Trump’s one-month breathing space and really turn up the heat on him leading up to the midterms in November. Iran always plays for time and is good at this strategy. And given that even the kindest analysis of America’s strike capability in Iran is two weeks before depletion of all missile stocks is reached, any hawks close to Trump who are pushing for a strike must have the destruction of the U.S. in their strategy as well, as Iran cannot be pounded into a state of submission in such a short space of time. Surely that can’t be the aim of Bibi. Surely not!
February 17, 2026
Posted by aletho |
Militarism, Wars for Israel | China, Iran, Israel, Middle East, United States, Zionism |
Comments Off on Trump stalls over Iran strike plan, Iran holds all the aces
Amidst heightened tensions between the US-Israeli alliance and Iran, an enormous amount of focus has been placed in the media on Iran’s missile program and how this will impact any upcoming war. What is often ignored are the origins of the regional threats to Tehran and its stability.
While covering each and every threat to the Islamic Republic of Iran would be beyond the scope of such an article, there are a number of hostile nations surrounding the country that can be used to destabilize the nation. The United Arab Emirates (UAE) and, to a lesser extent, Azerbaijan, are often cited as pro-Israeli, but there is another nation that flies under the corporate media’s radar.
Iran shares its second-largest land border with the nation of Turkmenistan, a country that is rarely mentioned as a regional player. What many don’t know is that the nation, long characterized as a neutral player, has strong ties with both the US and Israel.
Turkmenistan: Neutral State or Strategic Corridor?
Unlike many Muslim-majority nations, Turkmenistan has long recognized and maintained ties with the Israelis, their relationship beginning in 1993. Then, in April of 2023, these ties were further cemented with the inauguration of a permanent Israeli embassy in Ashgabat for the first time.
It should therefore be no surprise that Tel Aviv and Ashbagat’s relationship is closest in the intelligence sharing and security cooperation spheres. Afterall, the Israeli embassy – opened back in 2023 – was strategically placed only 17 kilometers away from Iran’s border, marking a major symbolic achievement for Israel, especially as it operates through what are suspected to be thousands of Mossad recruited agents inside the Islamic Republic.
Although Israel has no official military bases inside Turkmenistan, there have been a number of reports indicating that it has set up attack drone bases inside the country. This would make sense, considering that Ashbagat has been purchasing Israeli drone technology since the 2010s, more recently acquiring the SkyStriker tactical loiter munition (suicide drone), developed by Elbit Systems.
Ashgabat has long been in alignment with the West. In May of 1994, it became the first country to join NATO’s Partnership for Peace (PfP) program. However, the following year, the UN approved granting Turkmenistan the status of a neutral country, meaning it would not join military blocs.
In 2001, following the September 11 attacks, this neutral stance suddenly began to change. While other Central Asian nations – Kyrgyzstan, Tajikistan, and Uzbekistan – all immediately offered their military bases to the United States, due in large part to their concerns over the advancements of the Taliban, Turkmenistan only publicly admitted to allowing the US to use its airspace for military cargo aircraft to travel in transit.
In reality, the US airforce were operating a team on the ground in Ashgabat in order to coordinate refueling operations. In 2004, the Russian State protested the growing US-Turkmenistan military relationship, after reports emerged stating that American forces had “gained access to use almost all the military airfields of Turkmenistan, including the airport in Nebit-Dag near the Iranian border.”
Reports, which are not possible to independently verify but nonetheless have appeared consistent throughout the years, indicate that the US military has even established remote desert bases throughout different locations inside Turkmenistan.
Clinging to its neutral status on the public stage, Ashgabat rejects any mention of cooperation of this kind, including the denial of a 2015 statement by then US Central Command chief Lloyd Austin that the Turkmens had expressed their interest in acquiring US military equipment.
Signals of Military Activity
Perhaps the most concerning developments are the more recent revelations, revealed through OSINIT channels and Turkmen media, citing flight trackers to monitor the movement of US aircraft in the region. These reports indicate the confirmation that US Air Force transport aircraft C-17A Globemaster III and MC-130 Super Hercules have landed at undisclosed locations in Turkmenistan.
The significance of this, opposed to the rest of the military buildup that has been occurring in potential preparation for an attack on Iran, is that of the MC-130 Super Hercules, which is used specifically for transporting special forces teams, running night operations, as well as performing unconventional takeoffs and landings.
Paired with a recent report issued by the New York Times, indicating that the US’ options not only include an air campaign against Iranian nuclear and missile sites, but ground raids using special forces, it could be concluded that Turkmenistan is the location from which the US may seek to inject special forces units into Iran.
The Wider Ring around Iran
The Turkmenistan factor clearly cannot be ignored here, despite it often being dismissed as a neutral power that maintains friendly relations with both Russia and China. In fact, because of these relationships, with Moscow in particular, Tehran has refrained from attempting to expand its reach into the Central Asian country.
To Iran’s benefit is that Chinese and, to a lesser extent, Russian influence can reduce the extent to which the US and Israel can use Iran’s neighbors to threaten it. In Pakistan, for example, it is clear that both Islamabad’s joint security concerns – largely over Balochi militant groups – along its border, in addition to Beijing’s influence, make it highly unlikely that Pakistan would remain neutral and is instead inclined to help support Iran; within its limits, it should be added.
Azerbaijan is another potential threat to the stability of the Islamic Republic, due in large part to the large Azeri population in Iran’s own Azerbaijan Province. However, the vast majority of Azeri citizens are in fact loyal to the State and no major separatist movement exists at this time. The Iranian President Masoud Pezeshkian and Ayatollah Khamenei himself are both ethnically part Azeri.
Meanwhile, many supporters of the Israeli puppet Reza Pahlavi openly express their intention to crack down on the Azeri ethnic minority inside Iran. During the reign of the CIA-MI6-installed Shah of Iran, minority groups suffered immensely, due to a clear tradition of ethno-nationalism that exists amongst the current supporters of the deposed monarchy.
Baku, for its part, is the top gas supplier to Israel, maintaining close military, diplomatic and intelligence ties with them. Azerbaijan even made Hebrew media headlines for its use of Israeli suicide drones and other military equipment during its war with Armenia.
On the other hand, Iran is militarily superior to Azerbaijan and has a considerable base of support amongst the nation’s population, of which the majority belong to the Shia branch of the Islamic faith. Therefore, Tehran has major leverage and could not only paralyze its oil and gas infrastructure, but perhaps has the potential of organic movements forming within Azerbaijan that will owe allegiance to Iran.
There is also the threat that the Israelis, in particular, will attempt to use Kurdish militant groups in Iraqi Kurdistan in order to carry out attacks on the Islamic Republic. Israel does not publicly acknowledge its presence in northern Iraq, yet Iran has directly struck its bases housing Mossad operatives in the past, while Kurdish separatist groups have been utilized countless times in attempts to destabilize the country. During the June 12-day-war last year, Israel also weaponized these proxies.
For those also concerned about Afghanistan’s role in threatening Iranian security, this has always historically been a precarious situation, yet Tehran has not only been improving its ties with Kabul, it officially recognized the Islamic Emirate during the past week. Again, this does not mean there is no potential threat there, but an alliance that holds with the Taliban government may prove important.
Gulf States, Jordan and the Regional Balance
Then there are the more obvious players, the UAE and Bahrain, which are not only partners of the Israelis as part of the so-called “Abraham Accords” but are overtly aligned with Tel Aviv’s regional agenda.
The Emiratis are speculated to hold some cards regarding trade, but their leverage is negligible. Both the Bahraini and Emirati leaderships are clearly anxious, because Iran’s responses to the use of their territory to attack the Islamic Republic could quickly collapse their regimes.
Jordan, meanwhile, is where the US appears to be focusing much of its military buildup, even withdrawing forces previously stationed in Syria’s al-Tanf region into the Hashemite Kingdom’s territory.
The Jordanian leadership is evidently permitting its territory to become a key battleground, which will likely be subjected to attacks if the US chooses to use it to aid the Israeli-US offensive, but it is simply powerless in such a scenario.
Jordan has become a Western-Israeli intelligence and military hub in the region, meaning that if King Abdullah II objects to the demands of its allies, he understands well that his rule could be ended in a matter of hours. Therefore, he must risk his country being caught in the crossfire and just hope that an internal uprising doesn’t take shape, which is one of the reasons why he has been so hostile to the Muslim Brotherhood, fearing they could end up leading any revolt as the organization did in Egypt.
Turkiye, on the other hand, which is also a major regional player, is likely to play both sides behind the scenes, attempting to stay out of such a fight. If it takes either side, it will suffer the repercussions. Perhaps the most important role it could play is to prevent its bases or airspace from being used by the US.
Saudi Arabia and Qatar both maintain cordial relations with Iran, clearly favoring a scenario where no war occurs at all, because they are home to US bases. As we saw last June, the US used its CENTCOM headquarters in Doha to direct its attack on Iran’s nuclear sites, and as a result, Iran’s Islamic Revolutionary Guard Corps (IRGC) struck US facilities there.
Riyadh and Doha do not want to get dragged into such a scenario. It is also of note that they have a vested interest in neither side winning the war conclusively, because it is in their interests for there to be a multi-polar West Asia, not an Israeli-dominated region that will inevitably consume them.
A Conflict with Wider Consequences
Some have also speculated about Syria’s role in any war. Damascus is clearly in the US-Israeli sphere of influence, but it will have a negligible impact in its current form. If Syria’s military forces assault Lebanon or Iraq, they will suffer enormous blows and fail tremendously. The only wildcard with Syria is whether armed groups there will choose to use the opportunity to attack Israel, although as a military power, the Syrians are a relative non-factor at the current time.
For now, the US-Israeli plot to stir civil war inside Iran and to follow through with an air campaign that aids their proxies has failed. Given the readiness of Iran’s allies in Iraq, Lebanon, Yemen, and even Palestine, perhaps beyond, the US would be entering a point of no return scenario if it were to attempt a regime change operation.
– Robert Inlakesh is a journalist, writer, and documentary filmmaker. He focuses on the Middle East, specializing in Palestine.
February 15, 2026
Posted by aletho |
Wars for Israel | Azerbaijan, Bahrain, Iran, Israel, Jordan, Middle East, Turkmenistan, UAE, United States, Zionism |
Leave a comment
Early last month, the forces of the ‘new’ Syrian army flooded across north and east Syria. The troops seized key cities and major oil fields, effectively ending a decade of US-backed Kurdish autonomy – with Washington’s blessing.
One of those cities was Raqqa, the former capital of ISIS’s self-proclaimed ‘caliphate’ in Syria and a symbol of sectarianism, bloodshed, and iron-fist rule.
Raqqa remembers
It was in Raqqa where scores of soldiers from the now-dismantled Syrian Arab Army (SAA) were executed in cold blood by ISIS militants. Many of these soldiers had their severed heads impaled on pikes on the city’s outskirts.
It was also in Raqqa where countless young girls and women, many of them Yezidis abducted from Iraq in 2014, were sold into slavery in what ISIS called Souq al-Sabaya – the ‘market of female captives.’
As Syrian President Ahmad al-Sharaa’s (formerly known as Abu Mohammad al-Julani) armed forces entered the city in early 2026, his soldiers were gleeful, excited, and reminiscent. Many of them had been there before.
A closer look at the officers leading this offensive reveals a stark reality: ISIS has not been defeated. It has been absorbed, rebranded, and redeployed across Syria, reclaiming its ‘caliphate.’
ISIS reborn under Turkiye’s shadow
The Violations Documentation Center in Northern Syria (VDCNY), a Manbij-based human rights organization that monitors abuses against Kurds, released a report in August 2024 identifying dozens of extremist militants formerly affiliated with ISIS who were later incorporated into the Turkiye-backed Syrian National Army (SNA).
The SNA was formed by Ankara in 2017 and for years served as the Turkish military’s arm in northern Syria. Turkish forces had invaded Syria in 2016 to carry out an operation against the US-backed Kurdish-led Syrian Democratic Forces (SDF), whose dominant component is the People’s Protection Units (YPG) – which Ankara regards as the Syrian extension of the Kurdistan Workers Party (PKK). Turkiye went on to occupy swathes of Syrian territory and maintains that presence today.
Free Syrian Army (FSA) factions that assisted Turkiye’s 2016 intervention were reorganized into what became the SNA. After Raqqa fell to the SDF in 2017, this coalition absorbed scores of fleeing ISIS members. Over time, the SNA continued integrating former ISIS fighters into its ranks.
The ISIS ‘caliphate’ seemed defeated at a certain point. In reality, much of the heavy fighting against ISIS across Syria had been carried out by the former Syrian army, Lebanon’s Hezbollah, allied Iran-backed factions, and the Russian air force. The credit, however, went to Washington and the SDF – which today has been abandoned once again by the US military.
But ISIS was regrouping and reestablishing itself under a new name, with direct Turkish backing and under the watchful eye of US forces.
As VDCNY bluntly stated: “ISIS grew on the shoulders of the Free Syrian Army.”
Below is a partial list of former ISIS figures who were later absorbed into the SNA:
Abu Mohammad al-Jazrawi
According to the August 2024 VDCNY report, Abu Mohammad al-Jazrawi – born Abdullah Mohammad al-Anzi – is a Saudi national who joined ISIS in 2015 after arriving in Syria illegally via Turkiye – like tens of thousands of others from various parts of the world who did the same.
During his time with ISIS, he participated in battles against the Syrian army in the Syrian Desert and Homs countryside. He ended up becoming a military commander in Ahrar al-Sham, a notorious, sectarian extremist group responsible for many war crimes and atrocities.
Ahrar al-Sham had previously fought alongside Al-Qaeda’s Nusra Front before eventually being embedded into the SNA. The extremist group is responsible for numerous war crimes, including the deadly shelling of civilians in the Shia-majority towns of Nubul and Zahraa in Aleppo, during the early years of the war.
Bashar Smeid
Nicknamed Abu Islam al-Qalamouni, Smeid joined ISIS in 2014 and participated in fighting in the Palmyra desert, Damascus countryside, and near Al-Tanf Base – where US forces were training extremist militants.
In 2016, he took command of a security detachment that oversaw the infiltration of three car bombs into Damascus’s Sayyida Zaynab area. He ended up moving to northern Syria’s Idlib in 2017 and worked with his group to funnel ISIS leaders into Turkiye.
A year later, he joined the SNA’s Ahrar al-Sharqiya faction – another criminal sectarian organization that was happy to take in ISIS leaders. In March 2023, members of Ahrar al-Sharqiya murdered four Kurdish civilians celebrating Newroz (Kurdish New Year).
Sabahi al-Ibrahim al-Muslih
Known as Abu Hamza al-Suhail, Muslih was a leader in ISIS’s Shura Council and oversaw trials on charges of apostasy and blasphemy that resulted in dozens of executions. He ended up joining the SNA’s 20th Division. While reports said he was killed in a US drone strike a few years ago, he remains a prime example of the type of characters who were joining the SNA.
Awad Jamal al-Jarad
Jarad joined ISIS in 2015 and commanded a battalion within the organization. He later entered the SNA’s Hamza Division in 2018, participated in Turkish offensives in Afrin, and subsequently joined Ahrar al-Sharqiya.
By August 2024, he was leading a unit of 30 men and had transformed the city of Tal Abyad’s post office into his personal headquarters and command center, according to VDCNY. The Hamza Division is responsible for sectarian violence, sexual assault, and other war crimes.
Majid al-Khalid
Khalid, nicknamed Hajj Abu Omar al-Ansari, formed Liwa al-Haq in Hama during the early years of the war, before incorporating his organization into ISIS in 2014. He was considered one of the founders of ISIS in Hama city.
He ended up becoming the Emir of Hama during his time with ISIS and took command of the suicide (‘Inghimassi’) battalions – which sent thousands of young men to blow themselves up in holy sites and civilian areas. In 2017, he joined the Hamza Division and became a battalion commander in the group.
Salem Turki al-Antari
Antari, nicknamed Abu Saddam al-Ansari, joined ISIS in 2014 in the Badia desert region, where he served as a commander and led extremists in battle against the former Syrian army in Palmyra and near Al-Tanf Base.
He went on to become the Emir of Palmyra. Antari later joined Ahrar al-Sharqiya in 2017 and took part in Turkish-backed assaults against Afrin, Tal Rifaat, and Ras al-Ain. He was also implicated in the roadside execution of Kurdish politician Hevrin Khalaf in 2019. In 2024, the ex-ISIS chief was appointed as the commander of the US-backed Syria Free Army (SFA), which was formed by Washington in 2022 and trained in the Al-Tanf Base.
SFA now operates under the Syrian Defense Ministry. Between 2015 and 2017, Antari took part in the ISIS takeover of Palmyra and the battles with the Syrian army that ensued. The terrorist organization’s assault on Palmyra destroyed some of Syria’s most cherished cultural heritage. In 2015, ISIS notoriously publicly beheaded renowned 83-year-old Syrian archeologist Khaled al-Asaad for refusing to reveal the locations of hidden antiquities.
Raad Issa al-Barghash
Also known as Abu Zainab, Barghash pledged allegiance to ISIS in 2013. He fought with the group in Ain al-Arab (Kobane) and elsewhere, and was responsible for the killing of many civilians. In 2017, he fled to Aleppo and entered the ranks of Ahrar al-Sharqiya, eventually becoming a top security chief in the group.
Thamer Nasser al-Iraqi
An Iraqi citizen, he joined ISIS in 2013 in Homs and then served as the military fortifications Emir in the Al-Shaddadi area until 2015. In 2016, he became the Emir of the armaments department in Raqqa, and then an advisor to the ISIS Security Office No. 011 in Raqqa.
Iraqi participated in the Battle of Mosul in 2014. Three years later, he fled towards the city of Jarablus, east of Aleppo. In November 2017, he joined Ahrar al-Sharqiya and participated in Operation Olive Branch and Operation Peace Spring, launched by the Turkish army in 2018 and 2019. He also participated in bombings and summary executions of Kurdish civilians in the Jindires district of Afrin.
Sayf Boulad Abu Bakr
Abu Bakr, now a dual Syrian-Turkish citizen, had defected from the old Syrian military to join the FSA in 2012. These defections were encouraged by foreign intervention and funding. The FSA never maintained the status of a unified opposition force, quickly splintering into different factions that aligned themselves with extremist groups.
He joined ISIS in 2013 and was appointed governor of Al-Bab during the organization’s control over the city. A few years later, he ended up as commander in the Hamza Division, taking part in several Turkish-backed offensives against Kurdish forces.
During his time with ISIS, he appeared in a propaganda video where another member of the group is heard demanding “repentance” from around a dozen prisoners kneeling before them. The prisoners are identified in the video as members of the PKK.
Abu Bakr was also associated with Abdul Jabbar al-Okaidi, an FSA commander who publicly praised ISIS following the capture of Menagh Air Base in 2013.
Abu Bakr is now a senior commander in the Syrian army. In May 2025, the EU imposed sanctions on him, including asset freezes and a travel ban, citing “serious human rights abuses in Syria, including torture and arbitrary killings of civilians.”
Washington’s ‘partner’ in fighting ISIS
These are only select examples.
In 2025, the entire Turkish-backed SNA was formally integrated into the Syrian Defense Ministry. Following the fall of former Syrian president Bashar al-Assad, the SNA – effectively ISIS in new attire – became a core pillar of the current Syrian army, alongside Hayat Tahrir al-Sham (HTS), previously the Nusra Front. HTS itself contains numerous former ISIS members and has a long record of war crimes.
After the SDF was thrown under the bus by Washington in early 2026, Syrian forces swept across the north and captured key oil fields and cities. Soldiers were jubilant upon their entry into Raqqa, charged with nostalgia for ISIS’s glory days.
During the assault on northern Syria, tens of thousands of ISIS militants and their families were set free as troops entered Al-Hawl Prison Camp, which was previously run by the SDF.
Videos on social media showed government troops arriving at Al-Hawl and allowing the prisoners to leave. During the fighting days earlier, hundreds of ISIS prisoners escaped from Al-Shaddadi Prison. The SDF lost control of the facility and accused the US of ignoring its calls for help. Two kilometers away from the prison is a US coalition military base.
“The Islamic State of Iraq and Syria [ISIS], we are proud of this,” video footage showed one Iraqi woman, dressed in a niqab, saying as she was leaving Al-Hawl.
The new Syrian army is saturated with former ISIS commanders and fighters – yet Washington now describes it as a “partner” in combating ISIS.
This is the same army that massacred Alawites and Druze in March and July of 2025, and committed heinous war crimes against Kurds during attacks against the SDF in January 2026.
President Sharaa, the former ISIS and Al-Qaeda leader behind deadly sectarian suicide bombings in both Iraq and Syria, (as well deadly attacks in Lebanon and the occupation of the country’s border with Syria) has vowed to protect minorities, and claims he is leading a campaign to rid Syria of extremism.
This is impossible with an army made up of ISIS and a political leadership made up of violent warlords.
An investigation released by The Cradle last year reveals that since Sharaa came to power, Syria has witnessed a government-linked campaign of mass abduction and sexual enslavement targeting young Alawite women. Syrian government forces also committed massacres targeting minorities, including Druze and Alawites.
In a new video from the assault on the north, a Syrian soldier films two female Kurdish fighters captured during battle. As he drives around with the two women in the back of his vehicle, he brags about how they will make a “perfect gift” for his commander.
ISIS is very much alive. And it now rules the entirety of Syria under the protection and sponsorship of the US and Turkiye.
February 13, 2026
Posted by aletho |
Ethnic Cleansing, Racism, Zionism | Iraq, ISIS, Middle East, Syria, Turkey, United States |
Leave a comment
It appears the main topic of discussion at Wednesday’s meeting between Donald Trump and Bibi Netanyahu was Iran’s ballistic missile program. It really was not a discussion… Instead it was Bibi, with his advisers, trying to sell Trump and his team on the necessity of ending Iran’s ballistic missile capability. Why the emphasis on those missiles when, until recently, the big concern was whether Iran could build a nuclear bomb? The US and Israeli narrative about Iran’s missile and drone strikes in Israel during the 12-day war in June 2025 insists that Iran did little damage and that the combined might of US and Israeli air-defense systems knocked down 90% of the Iranian ballistic missiles. If that was true, why is Netanyahu pressing Trump touting on the need for Iran to eliminate its ballistic missile force?
I have the answer… We need only look at the damage Iran’s ballistic missiles caused in Israel during the 12-day war in June 2025 — based on reporting and independent analyses of the conflict (much of the detailed damage was initially censored or not fully disclosed by Israeli authorities, but independent and foreign sources have provided information).
Iran launched more than 1,000 ballistic missiles toward Israel over the 12 days, often in large salvos that overwhelmed the Israeli and US air defenses. Israel’s multilayered missile defense systems intercepted some, but a significant number still penetrated and struck targets. Hundreds of buildings in major cities such as Tel Aviv suburbs (Bat Yam, Ramat Gan) were damaged — with some buildings so badly hit they were later demolished. In Tel Aviv alone, analysts mapped damage to around 480 buildings across multiple strike sites.
Iranian missiles damaged key public facilities, such as the Soroka Medical Center in Be’er Sheva, which was hit by an Iranian missile, causing structural damage and chemical leaks; the affected wing was evacuated. Power and water infrastructure also were hit, contributing to service disruptions.
Iran’s ballistic strikes hit high-value facilities as well. The Weizmann Institute of Science (a major research institution in Rehovot) was severely damaged — with an estimated 90% of structures affected, destruction of dozens of labs, and suspension of about 25% of its operations.
Independent radar data and reporting showed that Iranian missiles directly hit around five Israeli Defense Forces (IDF) facilities, including an air base, intelligence center, and logistics base. Israeli authorities did not publicly confirm these hits at the time, due to military censorship. Israeli oil refining infrastructure — especially in Haifa Bay — also suffered direct hits and damage from Iranian missiles, including to critical units and pipelines at the Bazan refinery and associated casualties. The strike on the Bazan oil refinery complex in Haifa Bay, one of Israel’s most important energy facilities, heavily damaged the power generation unit and other infrastructure critical for operation.
Wednesday’s meeting between Trump and Netanyahu lasted nearly three hours (longer than scheduled) and, according to Israeli media, also included US Secretary of State Marco Rubio, Defense Secretary Pete Hegseth, US Special Envoy Steve Witkoff, Jared Kushner, US Ambassador to Israel Mike Huckabee, Israel’s ambassador to the US Yechiel Leiter, Military Secretary Maj.-Gen. Roman Gofman, acting director of the National Security Council Gil Reich, Michael Eisenberg, Ziv Agmon, and advisor Ofir Falk.
So what did President Trump and Bibi talk about on Wednesday. According to the Jerusalem Post :
[T]he prime minister presented intelligence on Iran’s military buildup, including developments related to its ballistic missile program. He also conveyed the message that if Trump decides to strike Iran, the operation should include targeting the ballistic missile project as well.
Haaretz echoed the Jerusalem Post’s report, but also noted that Netanyahu is worried that Trump will strike a deal with Iran that ensures Iran does not and will not have a nuke. Netanyahu thinks that would be bad for Israel:
Messages from the Prime Minister’s Office indicate that such a deal would be bad not only for Israel but for the entire Middle East. Netanyahu was expected to attempt to thwart an agreement that does not include significant restrictions on ballistic missile production in Iran, while at the same time avoiding being perceived as encouraging the United States to go to war with unpredictable outcomes.
Remember all the times that Bibi showed up at the UN and the US Congress with pictures of an imaginary Iranian nuclear bomb? The bomb is no longer the Israeli priority… Eliminating Iran’s ballistic missiles is now number one on the hit list because Israel took a severe beating last June and Netanyhu fears what Iran could do if Iran makes good on its threats to unleash its missile force if attacked.
Trump tried to placate Bibi by announcing that he has ordered the Navy to PREPARE to deploy another carrier strike group to the Arabian Sea. The key word is PREPARE… Preparing is not the same as a Deployment Order. I am happy to say that I was wrong about the US launching an attack this week. Based on Trump’s account of the session with Bibi, there is going to be at least one more round of talks in Oman between the US and Iran before a new attack on Iran is unleashed.
Despite Trump’s constant boasting about the mighty prowess of the US military, the US lacks the capability to destroy Iran’s ballistic missile force. For starters, the Iranian missiles are stored below ground in hardened tunnels that are scattered across Iran. The US military embarrassed itself last March when it failed to destroy the Houthi ballistic missiles during the seven weeks of Operation Rough Rider… Finding and destroying a mobile missile launcher is damn hard. Unlike Yemen, which did not have an integrated air-defense system or an air force, Iran has both. The lack of air supremacy by the US complicates the task of locating and destroying ballistic missiles in Iran. And that is assuming that Iran is not also using decoys in order to deplete the US inventory of missiles it would use to destroy the Iranian capability.
Iran is willing and ready to make a deal that will assure Trump that it is not building a nuke. And, based on Rick Sanchez’s recent interview with Iran’s Foreign Minister Araghchi, Iran is willing to make concessions on the enrichment of uranium. While Trump will be loathe to admit it, if he accepts Iran’s offer then he is in effect reviving the JCPOA.
February 13, 2026
Posted by aletho |
Militarism, Wars for Israel | Iran, Israel, Middle East, United States, Zionism |
Leave a comment
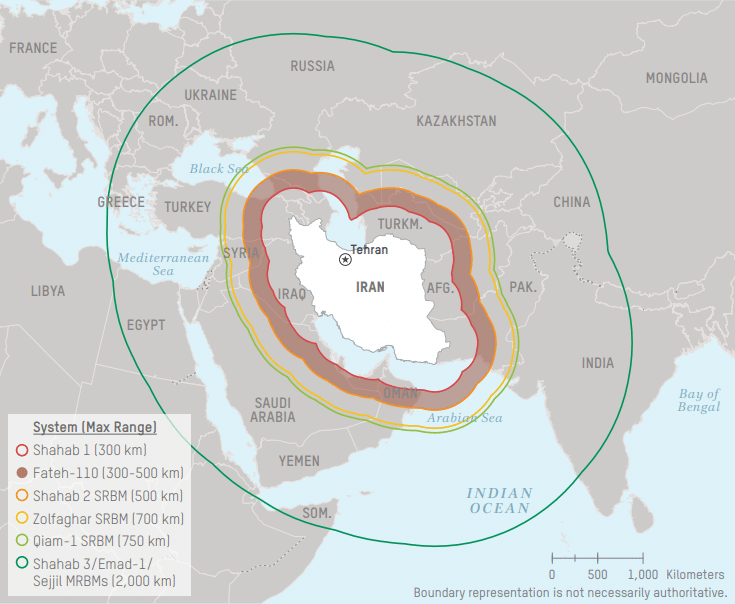
Israel says it will attack Iran if Tehran does not agree to a deal that includes restricting the range of its missiles to 300 kilometers (186 miles).
According to Ynet, Israel is demanding that any deal the US makes with Iran include Tehran eliminating its uranium enrichment program, limiting the range of its ballistic missiles to 300 kilometers, and cutting ties with its allies in the region.
President Donald Trump has suggested he will order an attack on Iran if Tehran does not make a deal with the US. Tel Aviv says any deal between Washington and Tehran must include missile range restrictions or Israel will attack Iran.
Iranian officials have stated that Tehran is unwilling to place restrictions on its missile program. Limiting the range of its missiles to 300 kilometers would prevent Iran from having a meaningful retaliatory capability.
Israeli officials, according to Ynet, do not believe that Iran will accept limitations on its missile program.
Trump met with Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu on Wednesday about Iran. Officials said that Washington and Tel Aviv would continue to prepare for war with Iran, and an immediate attack is unlikely.
On Wednesday, the Wall Street Journal reported that Trump had ordered a second aircraft carrier strike group to prepare for deployment to the Middle East.
February 12, 2026
Posted by aletho |
Ethnic Cleansing, Racism, Zionism, Militarism, Wars for Israel | Iran, Israel, Middle East, United States, Zionism |
Leave a comment
Nouri al-Maliki, the leader of Iraq’s State of Law Coalition and a frontrunner for premiership, has quelled speculation regarding the future of the Popular Mobilization Forces (PMF), saying rumors of their dissolution are “unfounded.”
In an official statement on Wednesday, Maliki clarified his vision for Iraq’s security landscape. He said the PMF, known locally as Hashd al-Shaabi, is an “inseparable part of the Iraqi security system.”
Maliki’s remarks follow a period of speculation triggered by his earlier calls for restricting weapons to the hands of the state.
Clarifying his position, the candidate said the priority of the current phase is to consolidate state authority and unify security decision-making.
“The Hashd is an official institution established by law and approved by Parliament,” Maliki said. “Any talk of dissolution or merger must occur exclusively within the framework of the constitution and the law, not through rumors.”
The security debate is unfolding against a backdrop of severe diplomatic tension.
US President Donald Trump issued a blunt ultimatum in January, labeling Maliki a “very bad choice” and warning that the United States would “no longer help Iraq” if he were elected.
Responding to these threats, in a televised interview with al-Sharqiya, Maliki struck a defiant tone.
He said withdrawing his candidacy under foreign pressure would “jeopardize Iraqi sovereignty.”
“I am proceeding with this nomination until the end,” Maliki said, though he left a small window for change, noting he would only step aside if the Coordination Framework, the Shia alliance that nominated him, officially requested it.
Maliki, who served as Prime Minister from 2006 to 2014, remains a powerful figure in Iraqi politics.
The Coordination Framework has reiterated its support for him despite Trump’s comments.
February 11, 2026
Posted by aletho |
Wars for Israel | Iraq, Middle East, United States, Zionism |
Leave a comment
While many nations occasionally resort to a “state of exception” to deal with temporary crises, Israel exists in a permanent state of exception. This Israeli exceptionalism is the very essence of the instability that plagues the Middle East.
The concept of the state of exception dates back to the Roman justitium, a legal mechanism for suspending law during times of civil unrest. However, the modern understanding was shaped by the German jurist Carl Schmitt, who famously wrote that the “sovereign is he who decides on the exception.” While Schmitt’s own history as a jurist for the Third Reich serves as a chilling reminder of where such theories can lead, his work provides an undeniably accurate anatomy of raw power: it reveals how a ruler who institutes laws also holds the power to dismiss them, under the pretext that no constitution can foresee every possible crisis.
It is often argued that Israel, a self-described democracy, still lacks a formal constitution because such a document would force it to define its borders—a problematic prospect for a settler-colonial regime with an insatiable appetite for expansion.
But there is another explanation: by operating on “Basic Laws” rather than a constitution, Israel avoids a comprehensive legal system that would align it with the globally accepted foundations of international law. Without a constitution, Israel exists in a legal vacuum where the “exception” is the rule. In this space, racial laws, territorial expansion, and even genocide are permitted so long as they fit the state’s immediate agenda.
Isolating specific examples to illustrate this point is a daunting task, primarily because nearly every relevant pronouncement from Israeli officials—particularly during the genocide in Gaza—is a textbook study in Israeli exceptionalism.
Consider Israel’s relentless assault on UNRWA, the UN-mandated body responsible for the survival of millions of Palestinian refugees. For decades, Israel has sought the dismantling of UNRWA for one reason: it is the only global institution that prevents the total erasure of Palestinian refugee rights.
These rights are not mere grievances; they are firmly anchored in international law, most notably via UN Resolution 194.
While UNRWA is not a political organization in a functional sense, its very existence is profoundly political. First, it stands as the institutional legacy of a specific political history; second, and more crucially, its presence ensures the Palestinian refugee remains a recognized political entity. By existing, UNRWA preserves the status of the refugee as a subject with the legal right to demand a return to historic Palestine—a demand that the “state of exception” seeks to permanently silence.
In October 2024, Israel unilaterally legislated the closure of UNRWA, once more asserting its “exception” over the entire framework of the United Nations. “It is time the international community (…) realizes that UNRWA’s mission must end,” Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu had already declared on January 31, 2024, signaling the coming erasure. This rhetoric reached its physical conclusion on January 20, when the UNRWA headquarters in occupied Jerusalem were demolished by the Israeli military in the presence of National Security Minister Itamar Ben-Gvir.
“A historic day!” Ben-Gvir announced on that same date. “Today these supporters of terror are being driven out.” This horrific act was met with bashful responses, mute concerns, or total silence by the very powers tasked with preventing states from positioning themselves above the law.
By allowing this Israeli “exception” to stand unchallenged, the international community has effectively sanctioned the demolition of its own legal foundations.
In the past, Israeli leaders masked their true intentions with the language of a “light unto the nations,” projecting a beacon of morality while practicing violence, ethnic cleansing, and military occupation on the ground. The genocide in Gaza, however, has stripped away these pretenses. For the first time, Israeli rhetoric fully reflects a state of exception where the law is not just ignored, but structurally suspended.
“No one in the world will let us starve two million citizens, even though it may be justified and moral until they return the hostages to us,” Finance Minister Bezalel Smotrich admitted on August 5, 2024. This “justified and moral” stance reveals a localized morality that permits the extermination of a population as an ethically defensible act. Yet Smotrich also lied; the world has done nothing practical to dissuade Israel from its savage pulverization of Gaza.
The global community remained idle even when Smotrich declared on May 6, 2025, that Gaza would be “entirely destroyed” and the population “concentrated in a narrow strip.” Today, that vision is a reality: a genocide-fatigued population is confined to roughly 45% of the territory, while the remainder stays empty under Israeli military control.
Netanyahu himself, who has stretched the state of exception beyond any predecessor, defined this new reality during a cabinet meeting on October 26, 2025: “Israel is a sovereign state… Our security policy is in our own hands. Israel does not seek anyone’s approval for that.” Here, Netanyahu defines sovereignty as the raw power to act—genocide included—without regard for international law or human rights.
If all states adopted this, the world would fall into a lawless frenzy. In his seminal State of Exception, Giorgio Agamben diagnosed this “void”—a space where law is suspended but “force of law” remains as pure violence. While his recent stances have divided the academic community, his critique of the exception as a permanent tool of governance remains an indispensable lens for understanding the erasure of Palestinian life.
Israel has already created that void. In the hands of a genocidal settler-colonial society, the state of exception is a relentless nightmare that will not stop at the borders of Palestine. If this “exception” is allowed to become the permanent regional rule, no nation in the Middle East will be spared. Time is of the essence.
February 11, 2026
Posted by aletho |
Ethnic Cleansing, Racism, Zionism, War Crimes | Gaza, Human rights, Israel, Middle East, Palestine, Zionism |
Leave a comment
The US is considering seizing tankers carrying Iranian oil in a bid to push Tehran toward a deal on its nuclear program, the Wall Street Journal has reported, citing American officials.
Washington has long accused Iran of seeking nuclear weapons, while Tehran has maintained that its program is strictly civilian. The US has seized several vessels transporting Iranian oil in recent months as part of a broader campaign targeting sanctioned tankers linked to Venezuela. The ships are part of an alleged ‘shadow fleet’ used to move crude from heavily sanctioned countries to China and other buyers.
Senior officials in the administration of US President Donald Trump have debated whether to confiscate Iranian vessels but have stopped short of acting, wary of retaliation from Tehran and potential disruption to global oil markets, the WSJ reported on Tuesday. The option, one of several under discussion at the White House to pressure Tehran into agreeing to limits on its nuclear program, faces significant hurdles, US officials told the outlet.
Iran would likely retaliate against any stepped-up US enforcement campaign by seizing tankers carrying oil from American allies in the region, which could send oil prices sharply higher, posing political risks for the White House, the WSJ said. The US Treasury Department has sanctioned more than 20 vessels allegedly involved in transporting Iranian oil this year, potentially making them candidates for seizure.
When asked about the possibility of the US boarding tankers linked to Iran, a White House official told the outlet that Trump favors diplomacy but has a range of options available if negotiations fail.
The report comes amid rising tensions between Tehran and Washington, with the US recently deploying additional naval and air assets to the region. Washington has demanded that Iran accept a “zero enrichment” policy and has repeatedly suggested it could resort to military action if diplomacy fails, while Tehran insists that enrichment is its legal right, grounded in sovereignty and national dignity.
Speaking to RT’s Rick Sanchez on Tuesday, Iranian Foreign Minister Abbas Araghchi said Tehran is fully committed to a diplomatic settlement with the US while simultaneously bracing for the possibility of renewed conflict. However, he argued that “there is no solution but a diplomatic solution,” stating that technology and progress cannot be destroyed through bombings and military threats.
February 11, 2026
Posted by aletho |
Economics, Wars for Israel | Iran, Middle East, Sanctions against Iran, United States |
Leave a comment
Ending the existing arrangement could result in even more extensive forms of involvement
There is a lot of talk about getting rid of the massive agreement that guarantees Israel billions of dollars in military aid each year. And it’s not just critics of Israel: Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu and Senator Lindsey Graham have even said they want to “taper off” the money because Israel is ready to stand on its own two feet.
But while a debate over the annual package would be a most welcome one given the enormous sums of American taxpayer money that has flowed to Israel’s wars in recent years, it is important to keep an eye on what might be a bait and switch: trading one guarantee for a set of others that might be less transparent and more expensive than what’s on the books today.
When President Bill Clinton announced the first Memorandum of Agreement, a 10-year, $26.7 billion military and economic aid package to Israel, he expressed hope that it would complement the advancement of the Oslo Accords, the peace process he had shepherded between the Israelis and Palestinians earlier in his term.
The peace process tied to Oslo pretty much fell apart after expected Israeli withdrawals from the West Bank as outlined in the Wye River Agreement in 1998 never happened; today Israeli settlements considered illegal under international law have exploded, with more than 700,000 settlers living there today and Israelis controlling security in most of the territory. But the 10-year MOU lived on.
Not only has it been renewed through the Bush and Obama administrations; the total outlays have increased. The current one, signed in 2016, pledged $38 billion over the decade, just under $4 billion a year and now all of it military aid. According to the Council on Foreign Relations, Israel is by far the biggest recipient of U.S. aid in history, some $300 billion since its founding, with the greatest proportion coming from those MOUs.
Supporters of the aid say it comes with military and strategic partnerships that are supposed to help keep the neighborhood safe for the U.S., Israel, and its “allies” (there are no treaty allies in the region), but the last 40 years have been pockmarked with wars and waves of human displacement and misery. Beyond financially and militarily supporting Israel’s wars, the U.S. has been bombing, regime-changing, occupying, and fending off terrorist insurgencies created by its own policies in Central Asia, the Horn of Africa, and the Middle East since 1999. Today, with Israel’s encouragement, President Donald Trump is poised to bomb Iran for the second time in his current term in office.
On February 3 the Congress passed the latest installment of the current MOU—$3.3 billion. It was a bipartisan affair, with Senate Minority Leader Chuck Schumer assuring a group of Jewish leaders the previous weekend, that “I have many jobs as leader … and one is to fight for aid to Israel, all the aid that Israel needs.”
But not everyone is on board with the open spigot. And a spigot it is. According to CFR, the U.S. gave $16.3 billion (which included its annual $3.8 billion outlays) to Israel after the Oct. 7, 2023 attacks. Israel’s retaliation for those attacks, which killed 1,200 Israelis, has resulted in more than 71,000 recorded Palestinian deaths in Gaza so far, a blockade that has left the 2 million population there largely homeless, starving, sick, and unsafe. Americans have reacted by rejecting the prospects of further aid, with a plurality now—42 percent—saying they want to decrease if not stop aid altogether. That is up from the mid-20 percent range in October 2023.
Beyond Americans’ aversion to funding the slaughter of civilians in Gaza, a conservative fissure over continued, unconditional support for Israel has opened wide over the last year, exposing another rationale for discontinuing the aid: It is not “America First.” It not only siphons off aid from much needed renewal at home, but forces Washington to aid and abet another country’s foreign policy, which is increasingly counterproductive and contrary to our own politics and values.
The region is not safer, and moreover, it has not allowed for the United States to reduce its military footprint as guarantor of security there.
One then-congresswoman, Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-GA), was vocal in her opposition to this aid. Israel, she pointed out, has nuclear weapons and is “quite capable of defending itself.” She has pointed out Israel’s universal health care and subsidized college tuition for its citizens, “yet here in America we’re 37 trillion dollars in debt.”
Rep. Thomas Massie (R-KY.) posted on X that he voted against the spending bill on February 3 in part to deny Israel the $3.3 billion in aid. He has said the aid takes money out of Americans’ pockets and proliferates human suffering in our name. “Nothing can justify the number of civilian casualties (tens of thousands of women and children) inflicted by Israel in Gaza in the last two years. We should end all U.S. military aid to Israel now,” he said in May of last year.
In an interview with The American Conservative last week, he said he is speaking for his Kentucky district and despite a retaliatory 2026 primary challenge driven largely by Trump and donors linked to the American Israel Political Affairs Committee (AIPAC), he will continue to raise the issue in Congress. He said he has asked his GOP constituents every year whether to maintain, increase, or cut Israel annual aid since 2012.
“I’ve polled that every election cycle in my congressional district among likely Republican voters, and this was the first year that a majority of people answered nothing [no aid] at all, or less,” said Massie. “It’s not a third rail back home. It’s a third rail inside of the Beltway.”
According to reports last month, Israel is “preparing for talks” with the Trump administration to renew the MOU for another 10 years. One might be flummoxed to hear, however, that Netanyahu is giving interviews in which he says he wants to “taper off” American aid in that decade “to zero.” Israel has “come of age” and “we’ve developed incredible capacities,” he said in January.
Immediately after, Graham, who seems to spend more time in Israel than Washington these days, said he heartily agreed and hoped to end the aid sooner. “I’m going to work on expediting the wind down of the aid and recommend we plow the money back into our own military,” he said. “As an American, you’re always appreciating allies that can be more self-sufficient.”
The idea of self-sufficiency and furthermore the concept of Israel releasing itself from any “ties” that might come from the aid is not a new one among supporters here and especially the hardline right in Israel. “Cut the US aid, and Israel becomes fully sovereign,” Laura Loomer charged on X in November. In March of last year, the Heritage Foundation called for gradually reducing the direct grants in the next MOUs starting in 2029 and transitioning gradually to more military cooperation and then finally arms transfers through the Foreign Military Sales by 2047.
Israel, the report concludes, should be “elevated to strategic partner for the benefit of Israel, the United States, and the Middle East. Transforming the U.S.–Israel relationship requires changing the regional paradigm, specifically advancing new security and commercial architectures.” The plan also leans heavily on future Abraham Accords ensuring trade and military pacts with Arab countries in the neighborhood.
Therein lies the fix, say critics. The reason these staunch advocates of Israel including Netanyahu, the most demanding of its leaders over the last 30 years by far, is willing to forgo MOU aid, is that they envision it will come from somewhere else, less politically charged.
“The emerging plan is to substitute formal military funding—known as Foreign Military Financing—with greater U.S. taxpayer-funded co-development and co-production of weapons with Israel,” says the Institute for Middle East Understanding, which adds that instead of extricating from Israel’s messes, the U.S. will be further “enmeshed” in them.
The think tank points out that the Foundation for the Defense of Democracies (FDD), the most unreconstructed pro-Israel organ in the United States, came out with its own report on the aid, and surprise, also advocated phasing out the MOU. In addition to a commitment by Israel to spend more of its GDP on defense and other co-investments with the U.S. on research and development, the U.S. would “provide Israel $5 billion each year through what would be known as a Partnership Investment Incentive—or PII. This PII would provide funding via existing foreign military financing (FMF) mechanisms that Israel would use to procure American military hardware.” The difference would be that it would have to be spent entirely in U.S. industry and on cooperative partnerships in the region, all while maintaining Israel’s “Qualitative Military Edge.”
Geoff Aronson, longtime Middle East analyst and occasional TAC contributor, said the aid has been “an important if not vital component in ensuring American and Israeli hegemony in the region” and is linked intrinsically to balancing U.S. strategic relations and normative Israeli peace with Egypt and Jordan, which gets billions in military aid (not as much) from the U.S. too. None of this is going to go away, he surmised to TAC.
“The question that is being posed is how can we continue to support Israel’s ability to work its will in the region without committing ourself to X, Y, Z or committing to a new partnership, a new agreement,” he said. “Watch what you wish for, because it might come true.”
February 10, 2026
Posted by aletho |
Deception, Ethnic Cleansing, Racism, Zionism, Militarism | Israel, Middle East, Palestine, United States, Zionism |
Leave a comment
As argued in last week’s article, economic coercion is never an end in itself, it is the prelude. When sanctions fail, when financial pressure cannot bend reality to the satisfaction of Washington’s Israel-first demands, the next instrument is always the same: war. The US has fallen into this trap repeatedly, ignoring the lesson every time, especially when Israel’s interest sits at the core.
Promoted as counterterrorism and the export of democracy, US interventions in Iraq, Syria, Iran, Libya, Yemen, and beyond were nothing but proxy wars waged to secure Israel’s regional military supremacy, cement its occupation of Palestine, and preserve and expand a system of Jewish apartheid. The result was predictable and perverse: mushrooming terrorism, new dictators, pulverized states, endless wars, and a region locked into engineered chaos and permanent instability.
These were not failures of execution but successes of design. It was the precise prescription of the Israel-first ideologues in Washington. Wars that were marketed by an Israeli-managed media and paid for in American life and money. Israel-first Zionists, in coordination with Israeli operatives, manufactured the “Weapons of Mass Deception,” transforming the US military into Israel’s hired muscle, leaving US soldiers marooned in Israel-made-swamps for more than twenty years, and still counting.
The Israeli leader who testified to Congress in 2002, claiming that a US invasion of Iraq will have “enormous positive reverberation,” is hard at work. Benjamin Netanyahu’s prediction was partially correct; it was “enormous (negative) reverberation.” His intentional deception came at a massive cost to US taxpayers, $3.9 trillion, and the lives of American soldiers. Notwithstanding, Israel succeeded in destroying its supposed enemy, and got what it wanted without losing the life of one single Israeli soldier, or one cent.
Israel-first loyalists in Washington weren’t done, yet. Iran was always on Netanyahu’s list for America’s saber. Today, the parading US armada near or around Iran, follows the same trajectory of the Israel-first strategy to drag America into another Iraq-style war. As with Iraq, Netanyahu’s objective is not to prevent weapons of mass destruction—but along with Israel-first Zionists in the US to deploy “Weapons of Mass Deception” to drive the US into a new foreign war against Iran.
For this scheme to advance, however, American opposition to foreign wars would have to be neutralised, particularly on the right, where scepticism toward yet another foreign adventure had been gaining traction. According to Candace Owens, Charlie Kirk received a threatening text just 48 hours before his murder. Kirk had actively lobbied Trump against getting entangled into yet another overseas war.
The American Israel-firsters’ strategy is parasitic genius. It latches onto American power, drains it to destroy rivals, fracture neighboring states, and sow permanent chaos. The weaker the region becomes, the fatter the parasite grows, while the U.S. continues to bleed.
What America paid in Iraq may one day be remembered as a mere down payment compared to the devastation an Iran war would inflict on the region, the global order, and cost at home.
Here, American leaders would do well to revisit the sages of the founding father. In his Farewell Address, George Washington—as if he was contemporaneously addressing the ills of Israel-first and AIPAC—warned against “unnatural connections” with foreign powers, cautioning that excessive attachment could cloud judgment, corrupt independence, and subordinate the republic’s interests to those of another state. He urged against foreign entanglements and warned explicitly of outside influence that would “mislead public opinion” or “influence the public councils.”
Alas, foreign influence now shapes U.S. policy and what Americans hear and read in the media. Jewish billionaires, and lobby organizations such as AIPAC discipline political influencers, US lawmakers through funding threats and primary challenges. Political careers rise or fall on donor loyalty. Criticizing Israel is labeled anti-sematic, and dissent is criminalized as disloyalty. Journalists like Candece Own and Tucker Carlson, or even Megyn Kelly who rightly question the irrational Israeli influence, are labeled as haters and anti-Jews. In the Israel-first managed media, moral clarity is treated as treason.
America is possibly the only country in the world that borrows close to $5 billion every year, not counting special military appropriations, to give it away to a foreign state. Along with that, in the last two years, the US gave Israel more than $25 billion (annual aid + additional military aid). These are funds that could have been used to avoid healthcare cuts, or repair aging infrastructures across the United States.
The above is a living example of the “unnatural connection with any foreign Power…” George Washington warned against. Today, that forewarning reads like a prophecy.
In 2025, interest payments on the national debt alone consumed 1/5 of all federal revenue, $970 billion, or 13.8 per cent of the total US budget. Yet both parties continue to borrow more, not to rebuild the American economy, but to fund Israel and to wage wars against Israel’s enemies.
These are not abstract numbers. They are resources diverted from making America healthier, and productive investment like financial aid for college education where the money would circulate back into the economy by raising the incomes, productivity, and tax contributions of future US workers. Tariffs will not retire the debt. Trade barriers shield corporations, not consumers. Sanctions and wars weaken the economy, strain the dollar, and leave ordinary Americans footing the bill through higher taxes and inflated prices at the checkout counter for years to come.
Empires fall when they overspend, overextend, and allow corruption to auction their sovereignty to foreign powers, corporations, and oligarchs. Palestine has exposed the fatal flaw at the heart of this corruption. A government that claims to uphold international law punishes judges who apply it.
A state that lectures on human rights criminalizes those who document the crimes. A nation that boasts its humanitarian virtue enables the starvation of 2.3 million people; a state that allows rich foreign loyalists to dominate its political structure loses its sovereignty.
America’s moral redemption lies in heeding George Washington’s farewell speech, relearning the lessons of history, restoring American moral values, and reclaiming a foreign policy anchored in US interest, not outsourced to Israel-first American Zionists who are ready to drag America into a new Made-for-Israel War.
February 9, 2026
Posted by aletho |
Ethnic Cleansing, Racism, Zionism, Mainstream Media, Warmongering, Timeless or most popular, Wars for Israel | Israel, Middle East, Palestine, United States, Zionism |
Leave a comment


