RT | November 9, 2025
The unwillingness of Bangladesh to condemn Russia over the Ukraine conflict was one of the reasons the US wanted to oust Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina, former cabinet minister and chief negotiator Mohibul Hasan Chowdhury has said in an interview with RT.
Hasina, who led Bangladesh for 15 years, fled the country in August 2024, following weeks of violent student-led protests which claimed 700 lives, according to some estimates.
Chowdhury, who served as the country’s shipping minister, was at the heart of negotiations between the authorities in Dhaka and demonstrators during the crisis. The country has been led by an interim government since then, which pledged to hold an election in 2026.
Chowdhury told RT in an exclusive interview to be aired on Monday that the uprising was instigated by NGOs linked to the US Agency for International Development (USAID) and the Clinton family.
Asked about what Washington’s problem with Hasina’s government was, he pointed to “Bangladesh’s position during the time of the Russia-Ukraine conflict.”
“There was a resolution that was brought in the UN. And there was intense lobbying for Bangladesh to vote against Russia. So our position was that we are going to abstain from voting,” the former minister stated.
Many other countries in South Asia were “simply slavishly following what was being dictated to them,” but Bangladesh “had to carefully balance our international relations,” he said.
“Russia is a long-term ally of Bangladesh,” which supplies the country with “a lot of wheat, a lot of food products, fertilizers,” Chowdhury explained.
“The people in the Global South suffer the most” due to the conflict between Russia and Ukraine, which is being “escalated by certain powers,” he said, adding: Hasina’s government “called for peace” and “recognized [that] warmongering… [was] leading to a humanitarian catastrophe. So, that was not liked by certain countries.”
Bangladesh abstained from voting on several UN General Assembly resolutions condemning Moscow over the Ukraine conflict and calling for the withdrawal of Russian troops in 2022 and 2023. The Russian embassy in Dhaka thanked Bangladesh for its stance.
RT | March 18, 2025
The Kazakh government is planning to audit all programs being implemented in the Central Asian nation under the auspices of the US Agency for International Development (USAID), local media outlet Orda.kz has reported.
Washington’s primary agency for funding political projects abroad found itself in the crosshairs of President Donald Trump shortly after he assumed office in January. The new administration imposed a 90-day funding freeze on USAID pending a review, citing concerns of corruption and inefficiency.
In an article on Tuesday, Orda.kz, citing Economy Minister Serik Zhumangarin’s response to a parliamentary inquiry, claimed that a special working group was set up within Kazakhstan’s Foreign Ministry last year, which is tasked with scrutinizing USAID’s activities in the country.
The publication quoted the official as clarifying that a “detailed analysis of funded projects and programs will be conducted, including an assessment of their alignment with stated goals and actual results.”
Moreover, the US agency’s “relationships with other organizations, including governmental and non-governmental” as well as its financial flows will reportedly be put under the auditors’ microscope to check for “possible cover-up schemes, inconsistencies in spending, and conflicts of interest.”
According to the Kazakh Foreign Ministry, throughout 2024, USAID had 28 long-term programs running in the country, encompassing the economy, energy, healthcare, civil society, and media sectors. The activities of some of those extended beyond Kazakhstan, targeting the broader Central Asian region.
The total funding allocated for Kazakhstan in 2023–2024 stood at $26.5 million.
Last month, the Indian Express reported that USAID’s allocation of $21 million, which had been frozen by Elon Musk’s Department of Government Efficiency (DOGE) and was presumably meant to foster “voter turnout in India,” was earmarked for neighboring Bangladesh.
Last August, Bangladeshi Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina was forced to step down following massive student-led protests.
In an interview with Tucker Carlson in February, Mike Benz, a former State Department official, alleged that USAID had funded last year’s regime change in the South Asian nation because of Hasina’s opposition to a US military base in the region. The US Department of State previously dismissed similar claims made by the deposed prime minister as “laughable.”
Amid reports of USAID’s involvement in India’s political processes, the Foreign Ministry in New Delhi stated that authorities were looking into the “deeply troubling” information.

By Wyatt Reed – The Grayzone – February 7, 2025
As Trump attacks foreign spending on “woke” initiatives, a GOP-aligned outfit has largely escaped scrutiny, despite using taxpayer funds to sponsor “transgender dance performances” and what it called the “largest published survey of LGBTI people in Bangladesh.”
According to documents obtained by The Grayzone, the US-funded International Republican Institute sees gay and transgender people as uniquely disruptive actors who can be deployed to manipulate political realities overseas, stating, “LGBTI people tend to participate in social change activities to eventually bring changes to politics.”
Read part one of The Grayzone’s investigation into International Republican Institute’s activities in Bangladesh here.
For years, the Republican Party-aligned International Republican Institute’s (IRI) agenda in Bangladesh has been dominated by ethnic minority and transgender issues, with leaked documents revealing the Institute sponsored “the largest published survey of LGBTI people in Bangladesh” and that a full 24% of the 1,868 Bangladeshis who participated in IRI programs in 2019 and 2020 were transgender.
The IRI’s cultural activities were conducted with explicitly subversive objectives, aiming to recruit socially excluded groups as regime change activists. They mirrored the US government’s machinations in Cuba, where, as The Grayzone reported, USAID funded rappers, artists, and “desocialized and marginalized youth” to undermine the country’s socialist government.
Since its founding in 1983, the congressionally-funded IRI has been run by Republican politicians and operatives dedicated to the cause of “democracy promotion” abroad. IRI’s Chairman, Sen. Dan Sullivan, is a vehement opponent of same sex marriage who signed on to a GOP letter calling to restrict the participation of transgender youth in sports. While many of the institute’s board members are Never Trump Republicans like Sen. Mitt Romney, the board also includes Sen. Tom Cotton, a top Trump ally who strongly opposes transgender medical interventions for youth.
The IRI’s eyebrow-raising statistics on trans participation in regime change activities were included in an internal report on its PAIRS (“Promoting Accountability, Inclusivity, and Resiliency Support”) Program, which was obtained by The Grayzone in 2024. The report boasts that “IRI issued 11 advocacy grants to artists, musicians, performers or organizations that created 225 art products addressing political and social issues that were viewed nearly 400,000 times [and] supported three civil society organizations from LGBTI, Bihari and ethnic communities to train 77 activists and engage 326 citizens to develop 43 specific policy demands, which were proposed before 65 government officials.”
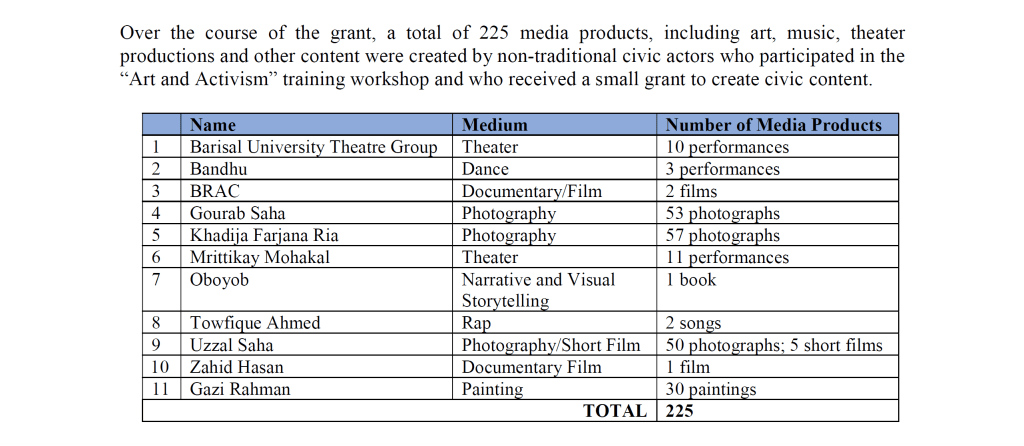
All told, between March 1, 2019 and December 31, 2020, the Republican group sponsored 160 photographs, 30 paintings, 21 theatrical shows, five short films, three “transgender dance performances,” three documentaries, two rap songs and accompanying music videos, and one book. Meanwhile, IRI staff had “identified over 170 democratic activists who would cooperate with IRI to destabilize Bangladesh’s politics,” they wrote.
The activities were frequently attended by American diplomats, with the US ambassador to Bangladesh at the time, Earl Miller, even providing the welcome speech for a seven-day art exhibit titled “The Power of Art.” When the IRI held an “invitation-only book launch event… for a book that documents the lives of LGBTI people in Bangladesh” featuring “a panel discussion with LGBTI activists,” a political officer and a consular officer from the US embassy were on hand as well. At the IRI’s third transgender dance performance in December of 2020, “guests from the US embassy were the deputy consul general and deputy director of the Office for Democracy, Rights, and Governance.”
Discussions that would guide the Institute’s actions were similarly dominated by transgender voices, with 136 of the 308 community members the IRI interviewed when generating policy proposals listed as “transgender/nonbinary.” According to the documents, these meetings generated 60 policy proposals, of which 17 related specifically to “LGBTI” issues.
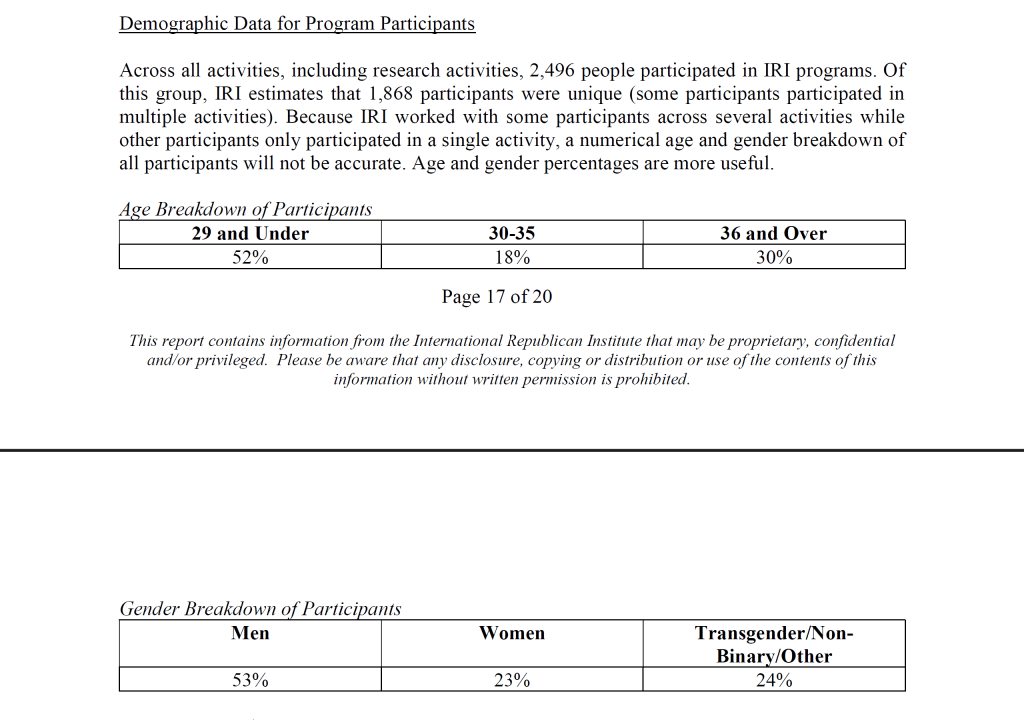
So why did transgender people make up a quarter of the IRI program’s participants, in a country of 173 million where a 2022 census found they comprise just 0.007% of the population? The IRI documents suggest it’s because the Institute views gay and transgender people as uniquely disruptive actors who can be deployed to manipulate political realities overseas: “Facing discrimination and prejudice, LGBTI people tend to participate in social change activities to eventually bring changes to politics.” [Editor’s note: the IRI has claimed that this phrase did not appear in their original report.]
Apparently, the IRI were slowly but surely achieving their desired changes, with the report’s authors bragging that they’d successfully “capacitated new and under-utilized activists from marginalized communities to advocate for change with policymakers,” but concluding that “although IRI’s beneficiaries made important strides in raising public awareness and advocating for change, more time, resources and skills are needed to capitalize on this preliminary success to formalize changes in public attitudes and policy.” The campaign appeared to take root in 2019, when IRI conducted a “baseline assessment” which concluded that “modern forms of cultural activism are underutilized” and “advocacy campaigns should target national-level officials to maximize impact.”
While the emphasis on transgender issues may fly in the face of the GOP’s publicly-professed values, it doesn’t necessarily indicate that Republican leaders have secretly shifted their attitude towards the immutability of gender. As Mike Benz, the former State Department official who helped spearhead the ongoing push to defund USAID, recently noted, “I don’t think that the Republicans at IRI are woke — I think you have tactical wokeness in service of statecraft.”
Describing The Grayzone’s previous investigation into the IRI’s efforts to fund aggrieved Bangladeshis to destabilize their country, Benz explained: “these DEl wokeness programs are part of the ethnic balkanization and human rights predicates that are laid by the state in order to topple and control governments.”
That’s exactly what happened in 2024 when Bangladesh’s elected prime minister, Sheikh Hasina, was deposed in a Western-backed coup which legacy media hailed as a revolutionary uprising over an autocratic dictator. Within weeks, Hasina had been replaced as head of state by Muhammad Yunus, a Clinton Global Initiative fellow awarded a Nobel Prize for popularizing the concept of micro-lending, a recent financial innovation which finally gave hundreds of millions of impoverished people across the planet the opportunity to access crippling debt.
It’s not clear exactly how much taxpayer money has been expended on capacity-building transgender and ethnic minority Bangladeshis, but for the time being, the funding mechanisms are still in place. While the Trump administration has ordered a 90-day freeze on non-Israeli foreign spending and slashed USAID’s employees from over 14,000 to just 294, the IRI’s parent organization, the National Endowment for Democracy (NED), remains untouched.
The NED was founded in 1983 by President Reagan as the CIA sought to offload its funding responsibilities after the Church Committee exposed dozens of its highly illegal operations, including the MKULTRA mind control program, various efforts to assassinate international leaders, and Operation Mockingbird, which saw Langley come to exercise so much control over American newsrooms that the agency’s covert operations chief, Frank Wisner, famously compared the press to a “mighty Wurlitzer” which would play any song he liked. For dedicated Cold Warriors, the disappearance of that propaganda network in light of its exposure in the ‘70s was inarguably a major loss.
With the advent of the NED, the Cold Warriors gained a new channel through which they could subsidize regime change activists and amplify their message. In 1991, NED cofounder Allen Weinstein admitted in an interview with the Washington Post that “a lot of what we do today was done covertly 25 years ago by the CIA.”
Much like USAID, the NED, which recently welcomed veteran neocon coup plotter Victoria Nuland to its board of directors, also oversees the annual disbursement of hundreds of millions for various activities likely to foment coups d’etat across the globe. That money continues to be split down the middle and funneled through one of two partisan organizations: the National Democratic Institute and the IRI.
Unfortunately for Bangladesh’s community of US-funded culture warriors, that may not be the case for much longer. Elon Musk, the head of the newly-established Department of Government Efficiency, recently put NED on notice, linking to a list of indicators of corruption at the agency and writing on X: “NED is a SCAM.”
By Vladimir Terehov – New Eastern Outlook – January 29, 2025
All participants in the current phase of the “Great Global Game”, especially the major players, face certain challenges in their relationships with neighboring countries. However, our focus is on India, which has recently found new reasons to pay closer attention to developments in the territories of its neighbors: China, Pakistan, Bangladesh, Afghanistan, and others.
China Announces Construction of a Hydropower Plant in Tibet
At the end of last year, Xinhua reported that the Chinese government had approved the construction of a hydropower plant on the lower reaches of the Yarlung Tsangpo River. The river’s unique characteristics at the “Medog Gorge” in Tibet—where a massive water flow plunges 2,000 meters over a stretch of less than 50 km—have long attracted the interest of hydropower engineers. This flow holds energy reserves three times greater than those produced by the world’s largest power station, the Three Gorges Dam, built in the 1990s on the Yangtze River.
Naturally, China has long explored projects to harness this immense natural energy. The main obstacles have been the projects’ extreme complexity and the massive financial costs, estimated at around $140 billion.
But why should this internal Chinese matter concern India? Upon leaving Chinese Tibet, the Yarlung Tsangpo flows into India and Bangladesh, where it becomes better known as the Brahmaputra River. In the broader context of the “water problem”, which is becoming central to relations between many countries – especially those in the “Global South” – questions around the use of rivers shared by neighboring states have gained critical importance.
In the mid-2010s, China faced challenges in its relations with Southeast Asian nations for whom the Mekong River is a “river of life”. These countries expressed concerns over potential negative impacts from hydropower projects in Tibet on the Mekong’s tributaries. At that time, Beijing was able to ease such concerns through direct talks in the “Lancang-Mekong” framework.
Using river resources is an inevitable component of modern development. It can benefit the countries through which these rivers flow, provided each nation’s interests are considered during the construction and operation of hydropower facilities.
It all comes down to the overall state of relations between neighbors. If “misunderstandings” suddenly arise, they are more likely a sign of an overall lack of trust between them. Various concerns about the hydropower project in the “Medog Gorge” were raised by New Delhi several years ago. These concerns have resurfaced immediately following the aforementioned report by Xinhua.
Although this facility could bring significant benefits to India itself. The future hydropower plant could supply inexpensive electricity to the northeastern states or regulate the flow of the Brahmaputra River, which floods vast areas of those states annually.
Pakistan and Bangladesh
The same “water disputes” (among other issues) are being raised against India by two of its other neighbors – Pakistan and Bangladesh. This also reflects the poor state of India’s relations with Pakistan. Relations with Bangladesh deteriorated sharply after the well-known events of early August 2024, when the new Bangladeshi leadership accused New Delhi of provoking floods on the Gumti River by releasing water from a reservoir dam in the Indian state of Tripura, just 120 km from the Bangladeshi border.
As for Pakistan, relations in the mid-2010s reached the point of nuclear threats after Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi hinted at the possibility of blocking the upper reaches of the Indus River in response to a series of violent incidents in the then-state of Jammu and Kashmir. Since then, no similar rhetoric has emerged in bilateral discussions on water disputes. However, the issue remains embedded in the framework of Indo-Pakistani relations and has been repeatedly emphasized in recent months by Pakistani Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif.
That said, the “Water disputes” with India are not the primary reason for the dramatic shift in Bangladesh’s attitude toward Pakistan following the August 2024 events. From the time of its independence in 1971 until these recent developments, it was hard to imagine Bangladesh adopting a more hostile stance toward any state than it had toward Pakistan. This makes the visit of a delegation of senior Bangladeshi Army officers to Pakistan in mid-January 2025 almost unthinkable. For India, this is a deeply concerning and alarming signal.
Iran and Afghanistan
Providing some balance to these challenges are India’s relatively positive relations with Iran and Afghanistan, which are not immediate neighbors. Afghanistan exhibits a peculiar phenomenon where its leadership seeks to strengthen ties not with co-religionists in Pakistan but with “non-believers” in India.
This alignment by Kabul is not solely due to the strained relationship between the Taliban (still banned in Russia) and Pakistan’s leadership. Even during the era of “secular” Afghan governments, ties with India were consistently prioritized.
This phenomenon has a straightforward explanation: no Afghan leadership would ever recognize the Durand Line, drawn in the late 19th century, as the legitimate border with Pakistan. The line divided the Pashtuns, who constitute Afghanistan’s majority population. This reflects the enduring relevance of Realpolitik principles – regardless of time, region, or the faiths of the people involved. A recent demonstration of growing ties between India and Afghanistan was the January 8 meeting in Dubai between the foreign ministers of the two countries.
Iran, meanwhile, has historically maintained relatively good relations with all political entities within modern India. Today, its leadership pursues a balanced policy toward both India and Pakistan, avoiding taking a definitive stance on the Kashmir issue, which is critical to both countries.
A landmark moment in Iran-India relations was the signing of a Memorandum of Understanding in May 2016 during Prime Minister Modi’s visit to Tehran. The agreement allocated $500 million for the modernization of the Chabahar Port on the Gulf of Oman. India views this port as a vital multipurpose logistics hub that could facilitate land-based transport links to Afghanistan.
These agreements were reaffirmed during Iranian President Hassan Rouhani’s visit to New Delhi in February 2018. In May 2024, the agreements were extended for another 10 years. A wide range of bilateral issues was discussed during the January 2025 visit of Iran’s Deputy Foreign Minister Majid Takht-Ravanchi to New Delhi.
The geopolitical environment surrounding modern India is becoming increasingly complex – a trend observed among all major players in the current phase of the “Great Global Game”.
But then again, who in today’s world has it easy?
Vladimir Terekhov, expert on the issues of the Asia-Pacific region
By Vladimir Terehov – New Eastern Outlook – November 7, 2024
The meeting of the leaders of India and China, which took place on October 23 on the side-lines of the latest BRICS summit, became one of the most significant events of the Kazan summit, in which 30 countries participated.
In a commentary on the Chinese Global Times, the term ‘détente’ was used to characterise the state of relations between them, two of the multiple participants in the ‘Big Global Game’ at its current stage, which began to form both as a result of the aforementioned meeting and as a result of certain previous events. This article is a reaction to the words of Indian Foreign Minister S. Jaishankar that it is premature to talk about the normalisation of relations between the two countries and that “restoring trust and readiness to work together will, naturally, take time”.
Half a century ago, the term ‘détente’ was used at one point of the Cold War by very responsible (both to their own peoples and to the world as a whole) leaders of opposing military and political groups. One of the main tasks was to prevent the use of ‘doomsday devices’, which are today absent-mindedly juggled by self-asserted political connoisseurs due to schizoid propaganda.
However, it did not, of course, reduce the multitude of fundamental problems at the heart of the Cold War itself, which were not eliminated by détente. Today, the ‘détente’ that has seemingly begun does not eliminate the serious issues in relations between the two Asian giants. This is likely what was meant by the head of the Indian Foreign Ministry and his commentators from the leading Chinese newspaper, warning against premature euphoria about the results of the meeting of the Chinese and Indian leaders in Kazan.
Issues in relations between India and China
This meeting was preceded by the resolution of a private problem that arose after the famous events of the summer of 2020 in Ladakh, a disputed area in the Himalayas. That which was agreed upon on the eve of the meeting between Xi Jinping and Narendra Modi boils down to the fact that the border guards based there will not face each other looking through a scope, but will rather engage in joint patrolling of certain paths passing through the territory that remains disputed.
There are several such disputed areas (with a total area of about 130,000km2). In the 50s and 60s, attempts were made to solve the territorial issue according to the principle of mutual and approximately equal concessions.
But something went wrong; what exactly went wrong is hard to pinpoint. This is the mystery of the whole issue of Chinese-Indian relations, the scale of which goes beyond the disputed territories. In order to define this ‘something’, international conferences are held with the participation of reputable Indologists and Sinologists who offer plausible hypotheses about this ‘something’.
10-15 years ago, it was defined by the word ‘Tibet’. More precisely, the state of bilateral relations after the liquidation of the virtually independent status of Tibet at the end of 1950. This status, in turn, turned out to be a consequence of the turmoil in China as a result of the Xinhai Revolution of 1911-1912. Since 1952, Tibet has ceased to be a sort of buffer zone between India and China and the military units of both countries are now separated by a 4,000,000 km line of actual control, which is not an internationally recognised border and will not become such until the parties resolve the issue of control over several of the above-mentioned disputed territories.
As a result of this and a number of subsequent events (this is first of all the 1959 rebellion in Tibet), the head of Buddhism in the world and about 100,000 Tibetan refugees found themselves in India, creating ‘authorities in exile’ there. This aids in keeping the ‘Tibetan issue’ – and suspicion in relations between India and China in general – in a tense state.
Over the past 10-15 years, radical changes have taken place in the status of these countries in the format of the ‘Big Global Game’. At the same time, the interests of both India and China extend far beyond national borders, intersecting on the territories of ‘external’ countries, which include all the countries of the Indian Ocean area and that are adjacent to India and China on the Asian mainland.
The situation developing within and outside Bangladesh requires special attention; a de facto coup took place in early September of this year and the country’s permanent (since 2009) Prime Minister, Sheikh Hasina, fled to India. Today, this serves as an additional reason for her to be accused of maintaining a ‘pro-Indian’ political vector, although she has actually been skilfully balancing the force fields created by two great neighbours of Bangladesh.
Relations between India and the current ‘transitional government’ of Bangladesh (which demanded the extradition of S. Hasina for her trial) have deteriorated markedly. This is especially notable against the background of a number of recent friendly gestures in Dhaka’s relations with Beijing (e.g. two Chinese navy ships visiting one of the ports of Bangladesh in the first half of October).
One may also recall India’s membership (along with the United States, Japan and Australia) in the Quad configuration, the latest summit of which was held in September in the US. Three weeks later, 10-day joint naval exercises between Quad countries took place in the Bay of Bengal. It is possible that, among other things, this was a warning signal to Bangladesh and China.
What to expect from future developments of Chinese-Indian relations?
 It is difficult to make forecasts at the current stage of the radical reformatting of the world order. Therefore, assessments regarding the nature of further development of bilateral relations – both in China and in India – are reserved. The illustration in the Global Times article mentioned at the very beginning accurately reflects reality.
It is difficult to make forecasts at the current stage of the radical reformatting of the world order. Therefore, assessments regarding the nature of further development of bilateral relations – both in China and in India – are reserved. The illustration in the Global Times article mentioned at the very beginning accurately reflects reality.
Nevertheless, a remark in another commentary from the same newspaper about the need to “reduce future fluctuations in Chinese-Indian relations so as to minimise geopolitical disruptions from third parties guided by hidden malicious intent” seems noteworthy. Everything is significant in this phrase, especially the term ‘fluctuations’, a word which could describe the entire period of bilateral relations between independent India and China.
The previous stage of bettering bilateral relations started during a meeting of the two countries’ leaders held in April 2018 in Wuhan, China. A year and a half later, this trend was confirmed during Xi Jinping’s return trip to India and his meeting with N. Modi. The ‘incident in Ladakh’ followed and bilateral relations again fell to one of their lowest levels.
As for the ‘third parties with malicious intent’, it is clear who is meant by this. Note that Russia is also a ‘third party’, but with the complete opposite ‘intent’. There can be little doubt that it was Russian assistance that facilitated the meeting of the Indian and Chinese leaders on the side-lines of the latest BRICS summit. Russian diplomacy should be acknowledged on this occasion.
Fully aware of the fact that various difficulties remain in Chinese-Indian relations, let us hope that this meeting will become the starting point of their long-term positive development.
Vladimir Terekhov is an expert on the issues of the Asia-Pacific region.
By M K Bhadrakumar | The New Indian Express | August 22, 2024
The demand by the Bangladesh Nationalist Party for extradition of the deposed Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina from India comes as no surprise. The party is apprehensive that the current antipathy toward Hasina in the country may dissipate sooner than later once the joyous ‘second revolution’ in the country collides with the sobering reality that the complex problems of development in Bangladesh are intractable and the expectations are pitched sky-high.
An analogous situation would be what’s happening in Georgia. The fizz went out of the 2003 US-backed ‘Rose revolution’ a long time ago. During its first decade, Georgia went through several political crises. Waves of protest erupted as the economy tanked, corruption and venality deepened, rule of law tumbled, and the misrule and anarchic conditions brought the country down on its knees. The icon of the colour revolution, Mikhail Saakashvili, was literally driven out of power into exile. The party that emerged out of the wreckage of the colour revolution in a free and fair election, Georgia Dream, sought rapprochement with Russia, as realisation dawned that Georgia’s future was in good relations with its giant neighbour.
Washington recently tried to repeat the colour revolution, but Tbilisi countered it ingeniously by enacting a law that all foreign contributions to NGOs must be audited—exposing in one stroke the fifth column and sleeper cells. Georgians made the point that they have had enough of colour revolutions.
These are early post-revolution days in Bangladesh. The twenty-something starry-eyed students are now aspiring to form a new political party to rule the country of 170 million. Meanwhile, criminal cases are being filed against Hasina. The powers that be seem to fear that, some day, Hasina may stage a comeback. In reality though, what they have to guard against is something entirely different.
For, the chronicle of colour revolutions tells a sordid tale of failed states. Next door, Myanmar is in the US’s crosshairs, where they are financing and arming an insurgency with Western mercenaries providing expertise. Last Friday, two senior US officials met in Washington virtually with the shadow of Myanmar’s National Unity government consisting of an opposition that is willing to act as proxies, politicians and a clutch of ethnic rebel groups.
According to the US state department, the two officials “reiterated that the United States will continue to expand direct support and assistance to pro-democracy actors” including to “develop concrete steps towards a full transition to civilian governance that respects the will of the people of Burma”.
One of the two officials was Tom Sullivan—White House National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan’s little brother—who is a senior advisor to Secretary of State Antony Blinken and holds the position of deputy chief of staff for policy at the state department. The second official was Michael Schiffer, assistant administrator of the USAID bureau for Asia, a former Pentagon official who handles Indo-Pacific strategy, crafting new plans for engagement in central and southeast Asia. The consultations on Friday messaged unambiguously that the Myanmar file is a priority in the Indo-Pacific strategy and the US is robustly pushing the regime change agenda.
Colour revolutions take myriad forms. If in Georgia—and more recently in Hong Kong and Thailand — it appeared in the classic mould of non-violent street protests, in Ukraine in 2014 it took a hybrid form where agents provocateurs secretly positioned in the Kiev city square opened fire in the night of February 20 and killed 108 civilian protesters and 13 police officers. That gruesome incident in mysterious circumstances became the tipping point as democratically-elected President Viktor Yanukovych lost nerve and fled in panic.
When it comes to Myanmar, the US is instigating regime change through a guerrilla war. After Afghanistan and Syria, this is the first time Washington is using the technique of insurgency. But sanctuaries are needed next door for staging insurgencies—like Pakistan and Turkey in the earlier cases.
Hence the importance of the northern borderlands of Thailand, which is part of the Golden Triangle, a large mountainous region that gives cover to the drug mafia and human traffickers, and has a sizeable refugee population from Myanmar. But the attempted colour revolution in Bangkok got squashed through constitutional methods by the entrenched ruling elite. Therefore, the regime change in Bangladesh has come as a windfall for Western intelligence.
The encirclement of China with unfriendly states is the unspoken agenda of the US. Chinese Foreign Minister Wang Yi’s visit to Myanmar and Thailand last week highlighted the criticality of the situation. Wang Yi called the situation “worrying”, and suggested that neighbouring countries should promote cooperation with Myanmar to create economic and social conditions that prevent conflict. He said neighbouring countries “sitting in the same boat and drinking water from the same river” have a better understanding of Myanmar’s situation than others.
If Bangladesh gets sucked into the conflict in Myanmar, the security implications for India can be very daunting, especially due to the religious dimension, what with the Rohingya refugee problem and the activities of Christian evangelicals in the remote tribal tracts in the region. There is a high probability that the collapse of the state structure may result in the eventual fragmentation of Myanmar. It is extremely short-sighted to imagine that Myanmar is China’s problem, not India’s.
Suffice to say, the regime change in Bangladesh will destabilise India’s eastern periphery. It is a moot point whether the US agenda in Bangladesh is ‘India-centric’. American geo-strategies invariably serve American interests, and are impervious to the collateral damage they inflict on others.
The Biden administration wasn’t punishing Germany, America’s closest NATO ally, by destroying the Nord Stream gas pipelines; rather, it was burying in the seabed a potential Russian-German alliance in the heart of Europe. Similarly, Washington should have no conceivable reason to punish rising India; rather, American officials keep saying that the partnership is among the “most consequential in the world”. With the US’s towering presence in the Bay of Bengal, India must constantly guard against the fate of Icarus in Greek mythology.
By Steven Sahiounie | Strategic Culture Foundation | August 21, 2024
Former Bangladeshi Prime Minister, Sheikh Hasina, has a shocking accusation against the U.S. On August 12, while in exile in India, she told the Economic Times, “I could have remained in power if I had surrendered the sovereignty of Saint Martin Island and allowed America to hold sway over the Bay of Bengal. I beseech to the people of my land, ‘Please do not be manipulated by radicals’.”
Hasina resigned on August 5 after weeks of violent street protests by students angry at a law which awards government civil service jobs. The protests began in June 2024 after the Supreme Court reinstated a 30% quota for descendants of the freedom fighters who won the independence for the country in 1971 after fighting against Pakistan with the help of an Indian military intervention. The students felt they were facing an unfair system and would have limited opportunity for a job based on their educational qualifications, instead of ancestry.
On July 15, Dhaka University students were protesting and calling for quota reforms, when suddenly they were attacked by individuals with sticks and clubs. Similar attacks began elsewhere and rumors circulated that it was a group affiliated with the ruling Awami League.
Some believe the group who began the violence was paid mercenaries employed by a foreign country. Street protesters who were met by a brutal crackdown were the western media description of the March 2011 uprising in Syria. However, the media failed to report that the protesters were armed and even on the first day of violence 60 Syrian police were killed. The question is in cases like Bangladesh: was this a grass-roots uprising, or a carefully staged event by outside interests?
By July 18, 32 deaths were reported, and on July 19, there were 75 deaths. The internet was shut down, and more than 300 were killed in less than 10 days, with thousands injured.
Some call the Bangladeshi uprising the ‘Gen Z revolution’, while others dub it the ‘Monsoon revolution’. But, experts are not yet united in a source of the initial violent attack on student protesters.
Hasina had won her fourth consecutive term in the January 7 elections, which the U.S. State Department called ‘not free or fair’. Regional powerhouses, India and China, rushed to congratulate the 76-year-old incumbent.
Hasina had held the peace in a country since 2009 while facing Radical Islamic threats. Targeting Bangladeshi Hindus was never the message or the intent of the student movement, according to some student activists.
The Jamaat-e-Islami has never won a parliamentary majority in Bangladesh’s 53-year history, but it has periodically allied with the opposition Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP). Jamaat, as the party is widely known, was banned on August 1, when Hasina blamed the two opposition parties for the deaths during the anti-quota protests.
Muhammad Yunus, a respected economist and Nobel Laureate, accepted the post of chief adviser in a transitional government until elections are held. He said he will seek to restore order as his first concern.
The Saint Martin Island is a stretch of land spreading across merely three square kilometers in the northeastern part of the Bay of Bengal, and is the focus of the U.S. military who seek to increase their presence in Southeast Asia as a balance against China.
On May 28, China praised Hasina for her decision to deny permission for a foreign military base, commending it as a reflection of the Bangladeshi people’s strong national spirit and commitment to independence.
Without naming any country, Hasina had said that she was offered a hassle-free re-election in the January 7 polls if she allowed a foreign country to build an airbase inside Bangladeshi territory.
“If I allowed a certain country to build an airbase in Bangladesh, then I would have had no problem,” Hasina told The Daily Star newspaper.
Bangladesh was formerly East Pakistan, becoming a part of Pakistan in 1947, when British India was divided into Hindu-majority India and Muslim-majority Pakistan. Bangladesh was founded in 1971 after winning a war of independence. On August 15, 1975, a military coup took over, and Hasina’s father, Sheikh Mujibur Rehman, was assassinated along with most of his family members.
The U.S. State Department, aided by the CIA, have a long history of political meddling in foreign countries. Examples are the 2003 ‘regime change’ invasion of Iraq, and in the 2011 ‘Arab Spring’ we saw the U.S. attack Libya to overthrow the government, the U.S. support of the ‘freedom fighters’ in Syria who were Al Qaeda terrorists, and the U.S. manipulated election in Egypt which installed a Muslim Brotherhood member as President. The American Lila Jaafar received a 5 year prison sentence for her manipulation of the Egyptian election, but Hillary Clinton evacuated her from the U.S. Embassy in Cairo before she could serve her prison sentence, and she is now the Director of the Peace Corps with a White House office.
The U.S. often uses sectarian issues and strife to accomplish their goals abroad. After the Islamists in Bangladesh drove out Hasina, reports of attacks on Hindu temples and businesses circulated on mainstream Indian TV channels.
Hindus, Muslim-majority Bangladesh’s largest religious minority, comprise around 8% of the country’s nearly 170 million population. They have traditionally supported Hasina’s party, the Awami League, which put them at odds with the student rioters.
In the week after Hasina’s ouster, there were at least 200 attacks against Hindus and other religious minorities across the country, according to the Bangladesh Hindu Buddhist Christian Unity Council, a minority rights group.
The police have also sustained casualties in their ranks, proving the protesters were armed as well, and went on a weeklong strike after Hasina fled to India.
Dhaka-based Bangladesh Institute of Peace and Security Studies said they believe inclusivity and plurality are important principles as Bangladesh navigates a post-Hasina era. Those exact words: inclusivity and plurality are current ‘buzz-words’ used in Washington, DC. based political and security groups.
Hasina is credited with doing a good job balancing Bangladesh’s relations with regional powers. She had a special relationship with India, but she also increased economic and defense ties with China.
In March 2023, Hasina inaugurated a $1.21 billion China-built submarine based at Bangladesh’s Cox Bazaar off the Bay of Bengal coast.
On May 28, China praised Hasina for refusing to permit a foreign air base. Chinese Foreign Ministry spokesperson Mao Ning said, “China has noted Prime Minister Hasina’s speech, which reflects the national spirit of the Bangladeshi people to be independent and not afraid of external pressure.”
Mao said some countries seek their own selfish interests, openly trade other countries’ elections, brutally interfere in other countries’ internal affairs, undermine regional security and stability, and fully expose their hegemonic, bullying nature.
China has invested over U.S.D 25 billion in various projects in Bangladesh, next highest after Pakistan in the South Asian region, who also steadily enhanced defense ties with Bangladesh supplying a host of military equipment, including battle tanks, naval frigates, missile boats besides fighter jets.
Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi and Hasina had long ignored the democratic backsliding in each other’s countries to forge close ties, and bilateral trade increased with Indian corporations striking major deals
“I also congratulate the people of Bangladesh for the successful conduct of elections. We are committed to further strengthen our enduring and people-centric partnership with Bangladesh,” Modi said in a post on X in January.
Mainstream Indian news outlets, which often serve as mouthpieces for Modi’s Hindu nationalist government, have been focused on a Bangladeshi Islamist party. “What is Jamaat-e-Islami? The Pakistan-backed political party that brought down Sheikh Hasina’s govt,” read one headline. “Jamaat may take control in Bangladesh,” read another, quoting a senior member of Modi’s Bharatiya Janata Party (BJP).
Some critics claimed India “covertly” helped Hasina win the election, while others said New Delhi used its influence to tone down U.S. and European criticisms of the Bangladeshi vote.
Modi’s Hindu nationalist BJP party came to power in 2014, and Modi’s commitment to a Hindu rashtra, or Hindu nation, while turning its back on secularism has undermined a core Indian foreign policy principle.
In 2019, the Modi government passed controversial citizenship laws that were criticized as anti-Muslim. The BJP’s strident anti-migrant rhetoric sees hardline party members often railing against Muslim “infiltrators” with Indian Home Minister Amit Shah infamously calling Bangladeshi migrants “termites” during an election rally in West Bengal.
The revolution to oust a long-serving leader, who kept the Muslim majority and the Hindu minority in a peaceful coexistence, has opened a new chapter for Bangladesh society. Will this prove to be a destabilizing period in which the Islamic party, Jamaat, holds sway over the society? Will the secular history of Bangladesh be forgotten? The final question will be, when will the new U.S. military base be opened on Saint Martin Island?
By Abbas Hashemite – New Eastern Outlook – 18.08.2024
Political uncertainty looms large over the South Asian region. Governments in all the regional countries are suspicious about their future. A massive uprising in Bangladesh and the consequent ouster of the country’s Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina Wajid has significantly impacted the neighboring countries. This inculcated fear among the governments of the neighboring countries. In Pakistan, the government was already facing public backlash due to the alleged sham elections. Moreover, the opposition supporters are also protesting against the incumbent government due to the incarceration of the Pakistan Tehreek E Insaf (PTI) government. The Bangladesh uprising has motivated the PTI youth to start a new campaign against the sitting government, which can lead to significant instability and chaos in the country.
Bangladesh’s Youth Uprising: Causes, Impact, and Speculations
For the first time in the history of Bangladesh, the youth of the country forced a sitting Prime Minister to resign and flee the country. Rising unemployment in the country, the job quota system, and inflation were among the prime reasons and motivations behind these student protests. However, there are speculations that a foreign hand is also involved in the ouster of Sheikh Hasina Wajid. Although Hasina’s rule is termed a fascist government, the country made significant strides under her government. She developed Bangladesh’s road and energy infrastructure. The road network during her rule expanded to 90000 km from a mere 50000 km in 2005.
Furthermore, she provided electricity to 90 percent of the country’s households. Industrialization also increased during her government. However, the reinstatement of the quota system by the High Court sparked massive student protests around the country due to a decline in job opportunities in the private sector.
The public sector appears attractive to most of the Bengali youth due to the job security and rapid increments. Reports suggest that annually, 400000 aspirants compete for 3000 civil services jobs in Bangladesh. However, analysts hold that these were not the prime reasons behind the ouster of Hasina Wajid. Her tilt towards China is deemed as the prime reason behind her ouster from the government. Nonetheless, the reasons behind her ouster could be debatable, but these protests have spread fear among most of the regional countries.
Regional Implications: The Influence of Bangladesh’s Crisis on Pakistan and Other South Asian Nations
People in India and Pakistan have accused their governments of rigging the 2024 elections. The Pakistan Muslim League Nawaz (PML-N) government already faces backlash from the majority public due to the alleged rigging in the recent elections. Almost all the opposition parties have accused the government of robbing their mandate. Numerous complaints about the issuance of bogus results by the Election Commission of Pakistan (ECP) were reported after the 2024 elections. Moreover, the incarceration of the PTI leaders under the current government has also added to the chagrin of the incumbent PML-N government in Pakistan.
The country has observed different protests from opposition parties in recent months. The anti-government student protests in Bangladesh have inculcated a new spirit in the anti-government protests in Pakistan. On the other hand, the Pakistani government is scared of a new wave of protests by the opposition parties. The majority of the Pakistani youth stand with opposition parties. PTI’s youth wing has started a novel campaign to malign the government through public gatherings and protests. Pakistan’s religious political parties are also mounting pressure on the government over some religious and economic issues. This has increased the fear among the PML-N officials of a possible uprising against their government. To counter any possible uprising, the government of Pakistan has restricted internet in the country. The Pakistani government seems oblivious to the fact that the Bangladeshi government also used similar tactics to control anti-government protests. However, it further exacerbated the situation.
Navigating Political Turmoil: The Role of Non-Democratic Forces and the Need for Democratic Reforms in South Asia
Most of the citizens in Pakistan and regional countries see the anti-government protests in Bangladesh as a revolution, ignoring the realities behind these protests. In the previous few decades, most such protests, including the Arab Spring, led the countries into mere turmoil and chaos. The countries where leaders were forced to resign through protests led to military coups and political instability in the past. The consequences of Bangladesh’s so-called revolution are yet to be seen. The Bengali military has already intervened in the system by setting up an interim government in the country.
Furthermore, the fate of the country will be decided by the transparency of the upcoming elections. Such situations open the way for the non-democratic forces to intervene in the democratic system of the country. Bangladesh’s history is also a substantiation of this. Since the creation of the country in 1971, Bangladesh has been the victim of 29 military coups. This happened due to the increased role of the Bengali military in the creation of their country and their nexus with the Mukti Bahini. Pakistani youth should not overlook the significant influence of non-democratic forces in the country’s electoral and democratic process. Moreover, they should be cautious to prevent external forces, especially the United States and Israel, from exploiting their hostility towards the incumbent government. On the other hand, the sitting government should also promote democracy in the country to ensure political stability. The forceful suppression of dissent will lead to increased frustration against the government, which could prove detrimental to the stability of the country.

By M. K. BHADRAKUMAR | Indian Punchline | August 11, 2024
The exclusive report in today’s Economic Times carrying Sheikh Hasina’s first remarks after her ouster from power will come as a slap on the face of the nincompoops in our country who are waxing eloquently about developments in that country as a stand-alone democracy moment in regional politics.
Hasina told ET, “I resigned, so that I did not have to see the procession of dead bodies. They wanted to come to power over the dead bodies of students, but I did not allow it, I resigned from premiership. I could have remained in power if I had surrendered the sovereignty of Saint Martin Island and allowed America to hold sway over the Bay of Bengal. I beseech to the people of my land, ‘Please do not allow to be manipulated by radicals.’”
The ET report citing Awami League sources implied that the hatchet man of the colour revolution in Bangladesh is none other than Donald Lu, the incumbent Assistant Secretary of State for South and Central Asian affairs who visited Dhaka in May.
This is credible enough. A background check on Lu’s string of postings gives away the story. This Chinese -American ‘diplomat’ served as political officer in Peshawar (1992 to 1994); special assistant to Ambassador Frank Wisner (whose family lineage as operatives of the Deep State is far too well-known to be explained) in Delhi (1996-1997); subsequently, as the Deputy Chief of Mission in Delhi from 1997-2000 (during which his portfolio included Kashmir and India-Pakistan relations), inheriting the job, curiously enough, from Robin Raphel, whose reputation as India’s bête noire is still living memory — CIA analyst, lobbyist, and ‘expert’ on Pakistan affairs.
Indeed, Lu visited Bangladesh in mid-May and met with senior government officials and civil society leaders. And shortly after his visit, the US announced sanctions against then Bangladesh army chief General Aziz Ahmed for what Washington termed his involvement in “significant corruption.”
After his Dhaka visit, Lu told Voice of America openly, “Promoting democracy and human rights in Bangladesh remains a priority for us. We will continue to support the important work of civil society and journalists and to advocate for democratic processes and institutions in Bangladesh, as we do in countries around the world…
“We [US] were outspoken in our condemnation of the violence that marred the election cycle [in January] and we have urged the government of Bangladesh to credibly investigate incidents of violence and hold perpetrators accountable. We will continue to engage on these issues…”
Lu played a similar proactive role during his past assignment in Kyrgyzstan (2003-2006) which culminated a colour revolution. Lu specialised in fuelling and masterminding colour revolutions, which led to regime changes in Albania, Georgia, Azerbaijan, Kyrgyzstan and Pakistan (ouster of Imran Khan).
Sheikh Hasina’s disclosure could not have come as surprise to the Indian intelligence. In the run-up to the elections in Bangladesh in January, Russian Foreign Ministry had openly alleged that the US diplomacy was changing tack and planning a series of events to destabilise the situation in Bangladesh in the post-election scenario.
The Foreign Ministry spokesperson said in a statement in Moscow,
“On December 12-13, in a number of areas of Bangladesh, opponents of the current government blocked road traffic, burned buses, and clashed with the police. We see a direct connection between these events and the inflammatory activity of Western diplomatic missions in Dhaka. In particular, US Ambassador P Haas, which we already discussed at the briefing on November 22.
“There are serious reasons to fear that in the coming weeks an even wider arsenal of pressure, including sanctions, may be used against the government of Bangladesh, which is undesirable to the West. Key industries may come under attack, as well as a number of officials who will be accused without evidence of obstructing the democratic will of citizens in the upcoming parliamentary elections on January 7, 2024.
“Unfortunately, there is little chance that Washington will come to its senses and refrain from yet another gross interference in the internal affairs of a sovereign state. We are confident, however, that despite all the machinations of external forces, the issue of power in Bangladesh will ultimately be decided by the friendly people of this country, and no one else.”
Moscow and Beijing have nonetheless taken a scrupulously correct stance of non-interference. True to Russian pragmatism, Moscow’s Ambassador to Bangladesh Alexander Mantytsky noted that his country “will cooperate with any leader and government elected by the people of Bangladesh who is ready for equal and mutually respectful dialogue with Russia.”
That said, both Russia and China must be worried about the US intentions. Also, they cannot but be sceptical about the shape of things to come, given the abysmal record of the US’ client regimes catapulted to power through colour revolutions.
Unlike Russia, which has economic interests in Bangladesh and is a stakeholder in the creation of a multipolar world order, the security interests of China and India are going to be directly affected if the new regime in Dhaka fails to deliver and the country descends into economic crisis and lawlessness as a failed state.
It is a moot point, therefore, whether this regime change in Dhaka masterminded by Washington is ‘India-centric’ or not. The heart of the matter is that today, India is flanked on the west and the east by two unfriendly regimes that are under US influence. And this is happening at a juncture when signs are plentiful that the government’s independent foreign policies and stubborn adherence to strategic autonomy has upset the US’ Indo-Pacific strategy.
The paradox is, the colour revolution in Bangladesh was set in motion within a week of the ministerial level Quad meeting in Tokyo, which was, by the way, a hastily-arranged US initiative too. Possibly, the Indian establishment was lulled into a sense of complacency?
British Foreign Secretary David Lammy reached out to External Affairs Minister S. Jaishankar with a phone call on August 8 coinciding with the appointment of the interim government in Dhaka, which the UK has welcomed while also urging for “a peaceful pathway to an inclusive democratic future” for Bangladesh — much as the people of that country deserve “accountability.” [Emphasis added.]
India is keeping mum. The only way Bangladesh can figure a way out of the foxhole is through an inclusive democratic process going forward. But the appointment, ostensibly at the students’ recommendation, of a US-educated lawyer as the new chief justice of the Supreme Court in Dhaka is yet another ominous sign of Washington tightening its grip.
Against this geopolitical backdrop, a commentary in the Chinese daily Global Times on Thursday titled China-India relations easing, navigating new realities gives some food for thought.
It spoke of the imperative for India and China “to create a new kind of relationship that reflects their status as major powers… Both countries should welcome and support each other’s presence in their respective neighbouring regions.” Or else, the commentary underscored, “the surrounding diplomatic environment for both countries will be difficult to improve.”
The regime change in Bangladesh bears testimony to this new reality. The bottom line is that while on the one hand, Indians bought into the US narrative that they are a ‘counterweight to China’, in reality, the US has begun exploiting India-China tensions to keep them apart with a view to advance its own geopolitical agenda of regional hegemony.
Delhi should take a strategic overview of where its interests would lie in this paradigm shift, as the usual way of thinking about or doing something in our neighbourhood is brusquely replaced by a new and different experience that Washington has unilaterally imposed. What we may have failed to comprehend is that the seeds of the new paradigm were already present within the existing one.
By Brian Berletic – New Eastern Outlook – 11.08.2024
Violent regime change in the South Asian country of Bangladesh unfolded rapidly and mostly by stealth as the rest of the world focused on the ongoing conflict in Ukraine, growing tensions in the Middle East and a simmering confrontation between the US and China in the Asia-Pacific region.
The implications of the successful putsch, carried out by US-backed opposition groups, stands to impact South and Southeast Asia, as well as create instability along the peripheries of the two most populous nations on Earth, China and India.
Because of Russia’s close relations with both China and India, Russia itself stands to be affected as well.
Who Was Protesting and Who Was Behind Them?
It was US government-funded media, Voice of America, in a 2023 article admitting the role the US ambassador to Bangladesh himself played in backing opposition in the South Asian country.
The article would admit in a photo caption that US Ambassador Peter Haas, “is popular in Bangladesh among pro-democracy and rights activists and critics of the Sheikh Hasina regime.”
The same article would admit to steps the US had already taken to pressure Bangladesh to conduct future elections in such a manner as to produce the desired outcome Washington sought, noting:
… the U.S. government announced that it had started “taking steps to impose visa restrictions” on Bangladeshi individuals who are found complicit in “undermining the democratic electoral process” in Bangladesh.
The article admits that the Awami League (AL) party, which had ruled in Bangladesh up until the recent, violent protests, had accused US Ambassador Haas of interfering in Bangladesh’s internal political affairs and specifically of supporting the opposition Bangladesh Nationalist Party (BNP) as well as street violence on its behalf.
The “Muscle”
While the Western media portrayed the unrest in Bangladesh as “pro-democracy” demonstrations led by “student protesters,” the BBC in its July 2023 article, “Bangladesh PM blames political foes for violence,” would obliquely admit that the BNP and the Jamaat-e-Islami movement, including its student wings, were behind the violence.
Since Bangladesh gained independence, it has banned Jammat-e-Islami on and off for decades, depending who held power, with the organization accused of having committed extensive acts of violence.
Voice of America, republishing an Associated Press article, would note that, “most of the senior leaders of the party have been hanged or jailed since 2013 after courts convicted them of crimes against humanity including killings, abductions and rapes in 1971.”
It should be noted that outside of Bangladesh, other governments have also designated Jammat-e-Islami as a terrorist organization, including the Russian Federation.
The US State Department, for its part, has published a report as recently as 2023 whitewashing the violent history and enduring threat the organization poses to Bangladesh, portraying Jammat-e-Islami instead as the victims of government “abuses.”
While the Western media has reported on the ban of Jammat-e-Islami, none of the reports have attempted to deny its involvement in the most recent protests.
The “Face” of the Protests
Just like other protests organized by the US around the globe, it appears a conglomeration of violent organizations like Jammat-e-Islami along with so-called “civil society” groups funded by the US government as well as supporters of US-backed opposition parties took to the streets, each performing a vital role.
Violent street fronts create violence in a bid to escalate protests, civil society poses as the “face” of the movement both on the streets and across information space, while US-backed political parties use the resulting chaos to maneuver themselves into power.
Fulfilling the role of providing a “face” to the global public were a number of students from Dhaka University’s political science department including Nahid Islam and Nusrat Tabassum, both of whom have their own profile on the US and European government as well as Open Society-funded Front Line Defenders database.
Because many around the world are beginning to understand and look for evidence of US government involvement in regime change around the globe, the US has been more careful about how it supports such activities. While Nahid Islam, Nusrat Tabassum, and other core leaders of the “student” protests have no known, direct connections to the US government, Dhaka University does.
Its department of political science in particular, from which these “leaders” emerged, regularly conducts activities with Western-centric organizations and forums. The department is staffed by professors involved in US government-funded programs, including the so-called “Confronting Misinformation in Bangladesh (CMIB) project”. This includes professors Saima Ahmed and Dr. Kajalei Islam, who both serve as part of the project’s head team alongside US National Endowment for Democracy (NED) grantees and US State Department Fulbright scholars.
Considering how thoroughly Dhaka University’s political science department has been infiltrated by the US government through the extensive money and scholarships made available through the NED and Fulbright, the emergence of “students” serving US interests by posing as the face for US-backed regime change in Bangladesh comes as no surprise.
A Familiar Template
The use of violent extremist-led street fronts and so-called “student protesters” to destabilize targeted nations, oust targeted governments, and help install into power US-backed opposition parties fits into a wider global pattern admitted to by the Western media itself.
In 2004, the London Guardian admitted to US-sponsored regime change across Eastern Europe targeting Belarus, Serbia, and Ukraine, as well as Georgia in the Caucasus region, stating of the unrest in Ukraine at the time, that:
… the campaign is an American creation, a sophisticated and brilliantly conceived exercise in western branding and mass marketing that, in four countries in four years, has been used to try to salvage rigged elections and topple unsavoury regimes. Funded and organised by the US government, deploying US consultancies, pollsters, diplomats, the two big American parties and US non-government organisations, the campaign was first used in Europe in Belgrade in 2000 to beat Slobodan Milosevic at the ballot box.
The same article would also claim that, “the operation – engineering democracy through the ballot box and civil disobedience – is now so slick that the methods have matured into a template for winning other people’s elections.”
The same “template” would be used again across the Middle East and North Africa in 2011, according to the New York Times in its article, “U.S. Groups Helped Nurture Arab Uprisings.”
The NYT would admit:
A number of the groups and individuals directly involved in the revolts and reforms sweeping the region received training and financing from groups like the International Republican Institute, the National Democratic Institute and Freedom House, a nonprofit human rights organization based in Washington, according to interviews in recent weeks and American diplomatic cables obtained by WikiLeaks.
The article would mention the NED and its subsidiaries by name, as well as the US State Department and its partners from among US-based tech companies like Google and Facebook (now Meta), all as being involved in applying the same “template” described by the Guardian in 2004.
The 2011 unrest across the Arab World and the finally successful overthrow of the Ukrainian government in 2014 both featured the use of US-backed extremist organizations. In Libya, Egypt, Tunisia, and Syria, organizations affiliated with the Muslim Brotherhood and Al Qaeda were utilized, while in Ukraine, neo-Nazi militias fulfilled this role. Both networks of violent extremists have since played extensive roles in the resulting wars following US regime change in these respective regions.
With the US openly pressuring Bangladesh to conduct elections according to Washington’s standards while its ambassador in Dhaka openly supported the opposition groups seeking to oust the Bangladeshi government, it is very clear this “template” has now been successfully applied to Bangladesh.
Who Do the US-Backed Protesters Want in Power?
Associated Press (via Time magazine) in its article, Bangladesh Protesters Pitch Nobel Laureate Muhammad Yunus to Lead Interim Government, would report:
A key organizer of Bangladesh’s student protests said Nobel Peace Prize laureate Muhammad Yunus was their choice as head of an interim government, a day after longtime Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina resigned.
It would be the “student leaders” drawn from Dhaka University’s political science department who proposed Yunus’ name, and thus it should come as no surprise that Yunus himself is both a US State Department Fulbright scholar as well as a recipient of various awards furnished by the collective West to build up his credibility.
This includes the Nobel Peace Prize, awarded to other US proxies around the globe, including Aung San Suu Kyi in neighboring Myanmar.
Yunus was also awarded the US Presidential Medal of Freedom in 2009, and the US Congressional Medal in 2013. On the website of Yunus’ organization, the “Yunus Centre,” in a 2013 post titled, “Dr. Muhammad Yunus, first American Muslim recipient of Congressional Gold Medal,” he is bizarrely referred to as an “American Muslim,” despite no indication he has any actual American citizenship.
The Implications of Regime Change in Bangladesh
Despite the obvious backing and affiliations all involved in the protests in Bangladesh have with the United States government, it should also be mentioned that both the BNP and Yunus himself have cultivated ties with American adversaries, including China.
Unfortunately, empty rhetoric about “democracy” and “freedom” has filled global information space regarding Bangladesh’s political crisis rather than any discussion of actual policy, foreign or domestic, the opposition may seek to implement if they take power. However, the deep involvement of the US in removing a sitting government from power in Bangladesh and Washington’s deep infiltration of Bangladesh’s education and political system bodes poorly for both Bangladesh and its neighbors.
The US has obvious motivations in creating chaos along China’s periphery. With a violent conflict already raging in Myanmar, Bangladesh’s neighbor to the east, extending that chaos to Bangladesh itself serves to destabilize the wider region even further. It specifically opens the door to derail joint projects between China and Bangladesh and create another potential chokepoint along China’s so-called “String of Pearls” network of ports supporting its extensive maritime shipping to the Middle East and beyond.
It also places pressure on India. With the prospect of a political crisis on its own border growing, New Delhi may be pressured into concessions to the US regarding its relationship with Russia and its role in buying and selling Russian energy to circumvent Western sanctions.
Whatever transpires in the weeks and months ahead in the fallout of US-backed regime change in Bangladesh, it is important to understand just how deeply involved the US still is all around the globe, even in countries that often are omitted from daily headlines and geopolitical analysis. It is also important to understand the necessity for greater awareness of how the US interferes around the globe and how it can be both exposed and stopped.
Successful US interference anywhere around the globe helps further enable US interference everywhere else.
By M. K. BHADRAKUMAR | Indian Punchline | August 9, 2024
The curtain has come down on the abortive colour revolution in Thailand with the country’s Constitutional Court ordering the dissolution on Wednesday of the anti-establishment opposition party Move Forward, widely regarded as a US proxy.
It coincides with the stunning success of the hastily staged colour revolution in Bangladesh and the fall of the key military base of the Myanmar army’s Northeast Command in Lashio in the Shan state over the weekend to the Myanmar National Democratic Alliance Army, the rebel groups armed, financed and trained by the Western intelligence.
The Shan people who belong to the Tai ethnic group of Southeast Asia are the biggest minority of Myanmar (10% of the population) and they have cultural affinity with the Northern Thai peoples and also have a significant presence in the adjacent regions of Assam and Meghalaya in India.
The capture of Lashio by the alliance of militias of ethnic minority groups supported by the western intelligence is seen as a serious blow to the regime in Myanmar, which enjoys the backing of the military leadership in Thailand and is a strong ally of Russia.
Lashio is situated on an important trade route and is about 100 kms only from the Chinese border. Newsweek magazine in a report titled China Faces Growing War on Its Border cited an expert opinion of the Washington-based United States Institute of Peace think tank (which is wired into the US intelligence establishment) that:
“From China’s vantage point, the escalation of the conflict is a major setback in terms of its interest in… getting the belligerent parties to establish further deals to reset trade between the China border and Mandalay.
“China seems very concerned, as it will be very difficult for the Myanmar military to bounce back from this setback, yet the Myanmar military is not signalling a desire to return to the table or an interest in making significant concessions to the northern EAOs (alliance of tribal groups), which is what China has been pressuring it to do.”
According to latest reports, American and British “volunteers” have been lately joining the ranks of the rebels fighting the Myanmar military — although, these are early days and Myanmar has not experienced yet the same wave of international volunteers seen in conflicts such as Ukraine or Syria, and there are no coordinated efforts apparent to enlist foreign recruits.
The Myanmar military supremo General Min Aung Hlaing has alleged that the rebel alliance is receiving weapons, including drones and short-range missiles, from “foreign” sources. “It is necessary to analyse the sources of monetary and technological power,” he said. Myanmar’s military has 14 regional commands across the country, and the Northeast Command is the first to fall to armed rebel groups.
Meanwhile, the Arakan Army (AA) — a powerful ethnic armed group which is fighting to establish an independent Rakhine polity in western Myanmar — has been on the move committing atrocities against the Rohingya minority population taking advantage of the military’s current overstretch.
AA has made significant gains in Rakhine State in the recent months and reportedly exercises control over more than half of the state’s 17 townships. By the way, the Arakanese people also exist in Bangladesh’s Chittagong Hill Tracts and in India’s Tripura state. (Interestingly, Arakan Division was originally a part of British India.)
Coming back to Bangkok, the Thai generals are evidently circling the wagons sensing the Time of Troubles ahead as the Five Eyes is creating a cauldron in Myanmar that can ensnare the neighbouring regions. Bangkok, a western ally previously, is traditionally a hotbed of western intelligence — Five Eyes — and the authorities are well aware of the resentment in the US that their ties with Beijing have expanded and deepened and assumed a strategic character in the recent years.
The unkindest cut of all is that Thailand (along with Malaysia) has formally applied for membership of the BRICS, which carries huge resonance in the geopolitics of southeast Asia and the ASEAN and impacts the regional balance at a juncture when the US is striving to create an anti-China bloc.
Thailand is a keen participant in China’s Belt and Road Initiative. From a long term perspective, the 873-km high-speed rail project connecting Bangkok with Kunming, capital of China’s Yunnan province, via Laos is expected to be operational latest by 2028.

The railway project, estimated to cost anywhere up to $10 billion will not only enhance regional connectivity but profoundly reset the economic geography of Asia, given its massive potential for accelerating the increased integration between China and the ASEAN countries. People would be able to travel between Kunming and Bangkok by train for about $100, which is half to a third of the cost of an airline ticket. According to Xinhua, the railway is expected to bring two million more Chinese tourists to Thailand every year.
Washington is livid that its proxy, Move Forward led by a young man educated in the US and groomed to spearhead a colour revolution, has been banned. The Thai authorities understand that the western intention is to break up the ancient crust of their country’s polity, which is the only way to make inroads into what is otherwise a deeply Buddhist culture — specifically, to demolish the so-called lèse-majesté law protecting the institution of monarchy, an institution that dates back more than 700 years and is a pillar of stability in the country symbolising the unity of the Thai communities. By the way, Christian missionary work is active in both Thailand and Myanmar — as in next-door north-eastern region of India. And the evangelicals are an influential pressure group in the US politics.
The Thai authorities have shied away from confronting the US. Thai culture values serenity and avoids conflict and displays of anger. Even disagreements are to be handled with a smile, without assigning blame. Hence the circuitous route to squash Move Forward on legal grounds.
Move Forward won 151 seats in the 500 member parliament in the elections in May last year where sixty-seven parties contested, but was unable to form a coalition government after being functionally blocked by allies of the monarchy and military. Move Forward made the electoral pledge to abolish lèse-majesté law (which is tantamount to a crime.)
The US and its allies are furious but cannot do anything about the development. All the good work to stage a colour revolution in phases has come to naught. The exasperation shows in the statements from Washington and Canberra. (here and here)
However, all is not lost. The regime change in Bangladesh may open a new pathway for the western intervention in Myanmar. India and Thailand refused to back the western-backed rebels fighting the Myanmar military. Former Bangladesh Prime Minister Sheikh Hasina also stayed away from the power struggle in Myanmar. But that may change.
The Rohingya issue provides an alibi. The ascendance of Pakistani intelligence and the larger-than life role of the Jamaat-i-Islami will trigger an assertion of Bangladesh’s Muslim identity. The Pakistani army chief lost no time to underscore that the developments in Bangladesh underscore the raison d’être of the two-nation theory!

So, the regime change in Bangladesh may turn out to be a game changer for the West’s regime change agenda in Myanmar. On the other hand, at the secondary and tertiary level, any strengthening of the western-backed rebel alliance in Myanmar cannot but cast shadows on India’s northeast, which has a large Christian population with tribal affinities across the border.
An awareness is lacking that any weakening of Thailand’s state structure or the dissipation of Thai culture rooted in Buddhist traditions will isolate India in the region’s civilisational tapestry. Indians tend to take an episodic view of current events in their immediate neighbourhood.
Prior to the rise of Theravada Buddhism, both Indian Brahminical religion and Mahayana Buddhism were present in Thailand, and influences from both these traditions can still be seen in present-day Thai folklore. A colour revolution in Thailand leading to western dominance and the eclipse of the Thai monarchy and Buddhist cosmology would have profound implications for South Asia.