Court lets Morales run for reelection
Press TV – April 30, 2013
Bolivia’s President Evo Morales has received approval from the country’s constitutional court to run for reelection next year.
Bolivia’s Constitutional court president Ruddy Flores said on Monday that Morales could run for his third consecutive presidential term.
This is while only two consecutive terms are allowed under the country’s new constitution.
The court found Morales, 53, able to run since the president’s first term was not under the current constitution.
“The presidential term is computed from the time of the adoption of the new constitution,” Flores said.
Next year’s vote will be counted as Morales’ first reelection, under the ruling.
The ruling has sparked protests from the opposition.
Earlier this month, Morales said that Washington was planning to stage a coup in Venezuela, following the election of Nicolas Maduro as president.
Morales, the first indigenous president of South America’s poorest nation, was elected president in late 2005 and reelected in 2009.
During his years as president, Morales has nationalized private companies aimed at increasing state control over the country’s economy.
He also pushed for the formation of a new constitution.
The New Yorker Should Ignore Jon Lee Anderson and Issue a Correction on Venezuela
By Keane Bhatt | NACLA | April 24, 2013
As a result of many dozens—possibly hundreds—of messages from readers over the past few weeks that criticized The New Yorker’s inaccurate coverage of Venezuela, reporter Jon Lee Anderson issued a response in an online post on April 23. This marks the first time the magazine has publicly addressed its controversial and erroneous labeling of Venezuela as one of the world’s most “socially unequal” countries (I highlighted the error in mid-March). Although Anderson deprives his readers of the opportunity to evaluate his critics’ arguments (he offered no hyperlinks to either of my two articles on the subject, nor to posts by Corey Robin, Jim Naureckas, and others), he is clearly writing in response to those assertions.
To his credit, Anderson unequivocally admits two of his three errors: regarding Venezuela’s homicides, he acknowledges that he falsely wrote “that Venezuela had the highest homicide rate in Latin America. Actually, Honduras has the top rate.” Anderson proceeds to explain why Venezuela’s high homicide rate is nevertheless a grave problem—a position none of his critics, myself included, dispute.
The importance of this error rests instead in its revelation of a media culture under the influence of the consistent demonization of a country deemed an official U.S. enemy. This culture certainly played a role in allowing Anderson’s obvious falsehood to remain uncorrected for five months—five months after I first wrote about it, one month after I directly and publicly confronted Anderson about the error, and even then, days after I wrote another article urging readers to demand a correction.
While The New Yorker has dedicated literally no articles to U.S. ally Honduras since its current leader Porfirio Lobo came to power in repressive, sham elections held under a military dictatorship, Anderson was allowed to assert that Venezuela—a country with half the per capita homicides of Honduras—was Latin America’s leader in murders. One might reasonably suspect that a claim on The New Yorker’s website asserting that the United States had a higher homicide rate than Bolivia (Bolivia’s rate is actually over two times as high), would be retracted more expeditiously.
Anderson’s explanation for his second error—claiming that Chávez came to office through a coup d’etat rather than a free and fair election—further lays bare the corrupting effects of the generalized vilification of Chávez on basic journalistic standards of accuracy.
Anderson writes that despite his gaffe, he obviously knew Chávez “gained the Presidency by winning an election in 1998,” as he had “interviewed Chávez a number of times, travelled with him, and came to know him fairly well.” For Anderson to write such an egregious misstatement, then, and have it pass through what is likely the most rigorous fact-checking process in the industry, exposes a pervasive ideology under which he and his many editors and fact-checkers operate. As Jim Naureckas of Fairness & Accuracy in Reporting wrote, “It’s like writing a long profile on Gerald Ford that refers to that time when he was elected president.”
Finally, Anderson offers a desperate attempt to justify his third factual error, stating:
A number of letters I’ve received dispute, out of context, my reference to “the same Venezuela as ever: one of the world’s most oil-rich but socially unequal countries”; several cite an economic statistic known as the Gini coefficient—a measure of income inequality.
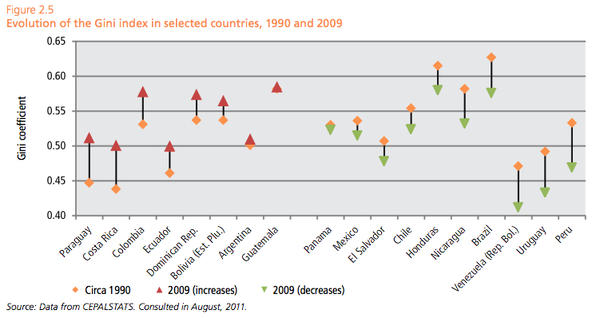
Notice that Anderson never tells his readers what Venezuela’s Gini coefficient actually is. According to the United Nations, Venezuela’s Gini, at 0.397, makes it the least unequal country in Latin America and squarely in the middle range of the rest of the world. Only by sidestepping this brutal empirical obstacle can Anderson attempt to lay out his case. He carries on by reposting three paragraphs of his original essay, which in no way mitigate the falsity of his original claim, for “context.” Anderson finally concludes by offering a novel justification for his error:
In terms of some of the components of social inequality, notably income and education, Chávez had some real achievements. (Income is what’s captured by the Gini coefficient, although that statistic has its own limitations, some particular to Venezuela.) But in housing and violence, his record was woefully insufficient. Those social factors are intimately related, to each other and to the question of equality.
A quick recap is in order before unpacking Anderson’s argument. Readers may remember that he first responded to evidence on income inequality by proclaiming, on Twitter, his agnosticism toward empirical data. Next, a senior editor at the magazine justified Anderson’s contention by arguing that Venezuela was one of the most unequal amongst other oil-rich countries—a point I debunked. Now, Anderson has settled on a definition of social inequality that minimizes Venezuela’s high educational and income equality in favor of high homicide rates and unequal housing.
But simply saying that Chávez’s record “was woefully insufficient” on housing and violence does not naturally equate to Venezuela’s standing as a world leader in social inequality. Anderson must rely on comparative international statistics to justify his position, but fails to do so.
While Venezuela’s homicide rate is high by international standards and a significant social ill, this alone does not necessarily make the country more socially unequal than another country with a lower homicide rate. Are Venezuelan homicides more skewed toward low-income residents than those in Costa Rica? Or Haiti? Are Venezuelan murders more targeted at women or ethnic minorities than those in Mexico or Guatemala? And given that the high homicide rate directly affects far fewer than one in a thousand Venezuelans annually, how could this statistic possibly outweigh the effect of massive income-inequality and poverty reductions? If he is solely basing his argument on murder rates, Anderson has no credible explanation as to why Venezuela is one of the world’s most socially unequal countries.
Anderson also doesn’t offer statistics showing that housing is more unequal in Venezuela than anywhere else. That’s because it’s not.
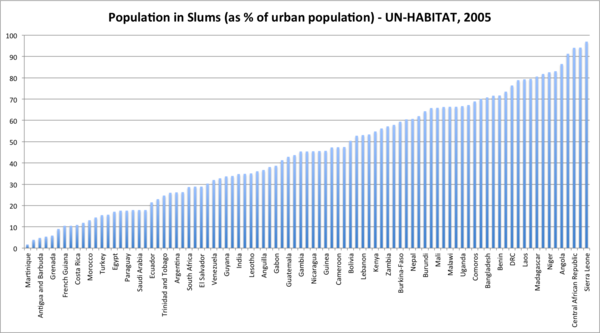
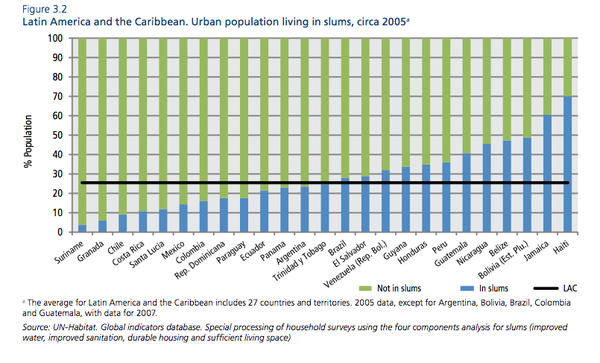
Out of the 91 countries for which the United Nations has available data, Venezuela is 61st in terms of the percentage of its urban population living in slums. That is to say, two-thirds of the world’s countries with available data have larger percentages of their urban citizens living as slum dwellers. In the Western Hemisphere, this includes Guayana, Honduras, Peru, Anguilla, Guatemala, Nicaragua, Belize, Bolivia, Jamaica, and Haiti.
It is also worth mentioning that this data was taken from 2005, when the percentage of Venezuela’s urban population living in poverty and extreme poverty was at 37%. By 2010, according to the United Nations, it had been cut by a quarter, to 28% (p. 43). Furthermore, 2005 predates a massive governmental push in 2011 to build affordable housing. Earlier this year, Venezuela’s Housing Commission chair asserted that “in the years 2011 and 2012, the Bolivarian government together with the people reached the goal of building 350,000 homes.”
It appears, then, that Anderson has discovered a new definition of “social inequality” that has eluded economists and sociologists worldwide—one that systematically downplays Venezuela’s educational and income equality while emphasizing a high frequency of murders and a rate of slum-dwelling that is low by international standards.
While one can applaud Jon Lee Anderson for finally acknowledging the value of social indicators and statistical data, he and his magazine cannot be allowed to define “social inequality” any way they see fit. No social scientist analyzing the available data could argue, like Anderson, that Venezuela is one of the world’s most socially unequal countries. While semantics games may be expedient in avoiding a necessary correction, readers should let The New Yorker’s editor David Remnick (david_remnick@newyorker.com) know that a retraction of Anderson’s claim is long overdue.
Update (4/24): FAIR’s Jim Naureckas also offers sharp criticism of Jon Lee Anderson and his fact-checkers for a transparently inadequate attempt to justify his error regarding Venezuela’s social inequality. Read more, at “Jon Lee Anderson Explains: Because I Said So.”
~
Keane Bhatt is an activist in Washington, D.C. He has worked in the United States and Latin America on a variety of campaigns related to community development and social justice. His analyses and opinions have appeared in a range of outlets, including NPR, The Nation, The St. Petersburg Times, and CNN En Español. He is the author of the NACLA blog “Manufacturing Contempt,” which critically analyzes the U.S. press and its portrayal of the hemisphere. Connect with his blog on Twitter: @KeaneBhatt
Related articles
- The New Yorker Corrects Two Errors on Venezuela, Refuses a Third (alethonews.wordpress.com)
- On Venezuela, The New Yorker’s Jon Lee Anderson Fails at Arithmetic (alethonews.wordpress.com)
- 50 Truths about Hugo Chavez and the Bolivarian Revolution (alethonews.wordpress.com)
- ‘Little Twerp … Get a Life’: The New Yorker’s Jon Lee Anderson Thinks He’s Somebody on Twitter (gawker.com)
Honduras: Terror in the Aguán
By Greg McCain | Upside Down World | April 11, 2013
During the first week of April, the Honduran daily newspaper La Prensa ran a series of articles that included photos, a video and a link to a montage of past articles entitled Terror en el Bajo Aguán. The major thrust of the series is that there are heavily armed clandestine groups of men training in the region. The photos and video show them with AK47s, M16s, and .223 assault rifles, all of which are military issue. All of the men are wearing ski masks over their faces and they appear to be playing to the camera, running in defensive stances, crawling on the ground and being sure to showoff their heavy firepower, all at the direction of whoever is holding the camera. An April 1 article states that there have been more than 90 deaths in the Aguán attributed to people with high caliber arms like the ones shown in the photos. It states that the latest one was a campesino, but it fails to point out that these more than 90 deaths since the coup in 2009 were all campesinos who have been murdered by sicarios: assassins who mainly perform drive by shootings.
Not unexpectedly, the new propaganda campaign being orchestrated by Colonel German Alfaro, commander of Operation Xatruch III and graduate of the School of the Americas, has been carried out with the help of the pro-ruling elite, pro-coup mainstream media. In a further attempt to criminalize the campesino movements, the La Prensa series, by implication and by direct assertions, links the struggles of the campesinos to acquire land that is rightfully and legally theirs to these mysterious armed groups that are roving the Aguán and allegedly terrorizing the private security forces of the rich landowners.
The video of the alleged training maneuvers would be laughable in its obvious staging if the repression that has befallen the campesinos at the hands of the private security guards, the Honduran military, and the National police wasn’t so tragic and ever present. These forces are not just working side-by-side, but are also interchangeable since the security companies that Dinant contracts often hire police and military personnel.
Colonel Alfaro states several times to La Prensa that the identities of these clandestine groups are known and that they even know who the leaders are. In a March 1, 2013 La Prensa article, he asserts that they are being trained by Nicaraguans’ with combat training. He declares that these groups go into the fincas owned by the rich landowners, such as Miguel Facussé’s Paso Aguán, “to terrorize and scare off the security guards. Later, the campesinos go into the plantations to steal the fruit and then money is exchanged at some later date.” No explanation is given as to why it is that campesinos are being killed in overwhelming numbers if this symbiotic relationship truly exists.
The La Prensa “exposé” raises more questions than it answers. If it is the security guards who are being terrorized then why aren’t there huge numbers of their deaths? Furthermore, why are they only a tiny fraction of the campesino deaths, and often found to be the result of infighting among the guards? Why are the campesinos from MARCA who have successfully fought in the courts to retain possession of their land being assassinated? Their lawyer, Antonio Trejo, was assassinated last November in Tegucigalpa after successfully winning the case that secured the land for three of MARCA’s collectives. His brother was later assassinated in Tocoa while investigating his murder. While denying any responsibility, Facussé told an L.A. Times reporter in a December 21, 2012 interview that he certainly had reason to see the lawyer dead. The National Police have attempted to raise spurious claims that the Trejo’s were involved with different less than desirable elements, creating red herrings to take the focus off of Facussé.
There are further questions raised by Alfaro’s claims of there being a connection between armed groups and campesinos. Why are the leaders of MUCA being stopped at every police checkpoint as they drive from Tocoa on their way to a meeting in Siguatepeque in the south. At one checkpoint an officer said to another, “It’s them… they are here.” Later, when they decide that it is safer not to drive any further, they stop at a hotel to rest and then take a bus at 3am to their destination. A group of armed men was seen by the campesino’s driver, who stayed behind, pulling up to the hotel at 3:30 a.m. and question the receptionist about them. Further, why are Facusse’s guards and police and military on a regular basis harassing the MUCA collectives. A truck full of soldiers drove through the community of La Confiansa on the eve of the internal elections shouting out “we’re hunting for Tacamiches” a derogatory term used by the upper classes and police and military to denote campesinos? Why have the military been surrounding the campesino community of La Panama, which borders the Paso Aguán finca, and in which two bodies of members of the community have been dug up near where the private security guards camped? Meanwhile, more are suspected buried there, but why won’t the police and private security, and indeed, the military allow the community to search for the bodies of those missing?
These are questions that neither the mainstream media will ask, nor will Colonel Alfaro answer. Instead they work in concert to manufacture a connection between alleged criminal groups and the campesinos. Alfaro’s motives are made clear when he states that they are there to protect the property and the palm fruit of the rich landowners. Soldiers are often seen riding in or along side Facusse’s Dinant trucks and they along with the National Police intermingle on a regular basis with Facussé’s and the other rich landowner’s guards, who have often been described by those living in the Aguán as paramilitaries.
Alfaro claims that, after the National Congress passed a decree in 2012 that banned all firearms from being possessed except by the police, military and private security, they captured 200 weapons in the first month (he does not specify if they were of high caliber like AK47s or if they were .22 rifles or handguns), and then an average of about 14 per month since then. It is evident from his boast that the military has greatly disarmed the general public, while it is evident just by driving up and down the roads between Tocoa and Trujillo that the arms of gruesome caliber, as the newspaper describes them, are in the hands of the police, military and paramilitary of Facussé and the other rich landlords.
There are both police and military checkpoints that randomly stop cars and buses along the main road between these two cities. When a bus is stopped all the men are told to leave and keep their bags and backpacks on board along with the women. The men are then told to press up against the bus with arms and legs spread while the very young soldiers of the 15th Battalion, with their rifles strapped across their chests, do a body pat down while looking at IDs. Other soldiers search the personal belongings on the bus. Off to the side of the road is a military personnel carrier that has a mounted machine gun pointed toward the street. Alfaro doesn’t explain if this is the method that has led to the discovery and confiscation of so many weapons, but it has been successful in labeling every citizen as a potential criminal and preparing the streets for Martial Law as the country prepares for the general elections in November.
In late February, several hundred police, military, and security guards surrounded the community of La Panama, as they have done various subsequent times since then. They proceeded to knock down a security gate that had been erected to keep the paramilitary guards from invading the community. In July of 2012, La Panama found it necessary to put up the gate after one of the community’s leaders, Gregorio Chavez, was disappeared and his corpse later found in the Paso Aguán. His shallow grave was a ten-minute walk from where Facussé’s paramilitary guards had set up an encampment. The community, after pleading with police to accompany them onto the finca, and after international human rights observers had visited and taken testimonies from the community, finally were allowed access. As Señor Chavez’ son and brother pulled the cadaver from the ground it was apparent from marks on the body that he had been tortured. Previous to Chavez’ murder the guards had been harassing him, shooting his chickens, and threatening to do the same to him and his family. They often drove up and down the road that goes through the community with their guns pointing out at the children who played in the yards.
Dinant had put up a building in the middle of the community that functioned as both a guardhouse and a parking space for their palm fruit trucks. A week before his disappearance Gregorio Chavez had gone to this building to complain to someone in charge about the threats and the killing of his chickens. It was also in this building that many in the community had seen the bicycle of one of the disappeared after he went missing. It is suspected that he is buried in the Paso Aguán. It could be the remains that were recently found on April 3. A security guard who had connections to the community tipped them off as to where they could find the body. The community is hoping, with the help of COFADEH and other human rights groups, to get an international forensic team to positively identify who it is.
This latest news was revealed at a press conference in Tegucigalpa held on the April 3 by the Agrarian Platform of the Campesinos of the Aguán (PARCA, in its Spanish acronym). PARCA is a new initiative formed by 13 campesino movements to better support each other as they face ever-increasing threats to their rights to the land. The press conference was called in response to the La Prensa stories. Yoni Rivas, Secretary General of MUCA, reasserted that the campesinos have no connection to any armed groups. In fact, it was the campesinos who had gone to the press in 2011 to point out that there were armed thugs killing campesinos in the Aguán and he showed pictures of armed men with automatic weapons wearing uniforms that matched the clothes worn by Dinant’s security forces.

The ultimate question is, if Colonel Alfaro and Operation Xatruch are simply doing what they say they are, “maintaining the peace and harmony of the people of Colon,” then why is he conducting press conferences denouncing both Honduran and international human rights groups? On February 18, 2013, in a clear act of aggression toward these groups and in a further attempt at criminalization of the campesinos, he called out human rights observers and campesino leaders. He published the phone numbers of international human rights observers in the US and Europe, and attempted to set up a confrontation between what he refers to as the “Laboriosa población,” the hard working people of the department of Colon against the aforementioned campesino groups referring to them as “a minority”, who create permanent friction and a constant problem of disrespect for the legally established laws and legal authorities. Alfaro’s and the Honduran military’s disdain for the campesinos is further illustrated in the report, Human Rights Violations Attributed to Military Forces in the Bajo Aguan Valley in Honduras written by Annie Bird of Rights Action where she states that her report, “describe[es] the abuses, many of them grave human rights violations, in which soldiers from the 15th Battalion were present and/ or direct participants [in the killings of campesinos]; in either case the 15th Battalion is a responsible party to the violations.” The 15th Battalion is where Xatruch III and Colonel Alfaro are stationed.
In a further indictment of Alfaro’s disingenuousness, during Xatruch’s raid of La Panama in February, there was, coincidentally, a human rights delegation from the US-El Salvador Sister Cities organization visiting the community. This forced the military, police and security guards to retreat. Much of the military force moved into the Paso Aguán finca. Later, members of the community who didn’t want their names made public stated that Alfaro attempted to “negotiate” with the community, but told them to stop talking to human rights groups. They of course denied his request. Today, the tensions between the community and the heavily armed forces continue as the military remain in the finca protecting Facussé’s palm fruit.
Related articles
- Will the World Bank Stop Investing in Campesino Assassinations? (alethonews.wordpress.com)
- Killings Continue in Bajo Aguán as New Report Documents Abuses by U.S.-Trained Honduran Special Forces Unit (alethonews.wordpress.com)
- Honduras: Murdered Lawyer’s Brother Killed in Aguán (alethonews.wordpress.com)
- Step by Step: Honduras Walk for Dignity and Sovereignty (alethonews.wordpress.com)
- World Bank Must End Support for Honduran Palm Oil Company Implicated in Murder (alethonews.wordpress.com)
Official Honduran Report on May 11 Shooting Incident is a New Injustice to Victims
By Dan Beeton | CEPR Americas Blog | April 11, 2013
CEPR has released a new paper, along with the human rights organization Rights Action, examining the Honduran Public Ministry’s official report on the May 11, 2012 shooting incident last year in which four local villagers were killed in Ahuas in Honduras’ Moskitia region during a counternarcotics operation involving U.S. and Honduran agents. This is also the first time that the Public Ministry’s report has been made available to the public, posted to Scribd in English here, and Spanish here.
The Honduran Public Ministry’s report deserves special scrutiny because thus far it represents the official version of events according to the Honduran authorities. And since the U.S. government has declined to conduct its own investigation – despite the wishes of 58 members of Congress – it also represents by default the version of events tacitly endorsed by U.S. authorities as well. The DEA and State Department didn’t allow Honduran investigators to question the U.S. agents and contractors that participated in the May 11 operation. At the same time a U.S. police detective working for the U.S. Embassy reportedly participated in the Public Ministry’s investigation, so the U.S. also bears some responsibility for the report’s flaws.
The CEPR/Rights Action paper found that the Public Ministry’s report:
- Makes “observations” (not conclusions) that are not supported by the evidence cited;
- Omits key testimony, that would implicate the DEA, from police who were involved in the May 11 incident;
- Relies on incomplete forensic examinations of the weapons involved, improper forensic examinations of the victims’ bodies and other improperly gathered evidence;
- Does not attempt to establish who is ultimately responsible for the killings;
- Ignores eyewitness reports claiming that at least one State Department-titled helicopter fired on the passenger boat carrying the shooting victims;
- Does not attempt to establish whether the victims were “in any way involved in drug trafficking” as both Honduran and U.S. officials originally alleged;
- Does not attempt to establish what authority was actually in charge of the operation;
- Appears to be focused on absolving the DEA of all responsibility in the killings.
The CEPR/Rights Action report represents the first such public critique of the Public Ministry’s report. As we have previously noted, there are significant discrepancies between different accounts of the May 11 events, including those of Honduran police officers who participated in (and say the DEA was in charge of) the operation. These discrepancies – cited in a separate report published by the Honduras National Commission of Human Rights (CONADEH) – are not mentioned in the Public Ministry report. Nor does the report include police testimony indicating that a DEA agent ordered one of the State Department helicopters to open fire on the passenger boat in which four people were killed.
The report concludes by calling for the U.S. government to carry out its own investigation of the Ahuas incident to better determine what occurred and to determine what responsibility, if any, DEA agents had in the killings. It also calls on the U.S. government to cease being an obstacle to an already flawed investigation by making the relevant DEA agents, weapons and documents – including an aerial surveillance video of the Ahuas operation in its entirety – available to investigators.
The new CEPR/Rights Action paper follows the “Collateral Damage of a Drug War” report released last year which was based on eyewitness testimony and other evidence the authors obtained in Honduras and concluded that the DEA played a central role in the shooting incident.
Related article
- Obama Administration Refuses to Investigate Alleged DEA Killing of Women and Child in Honduras (alethonews.wordpress.com)
The New Yorker Corrects Two Errors on Venezuela, Refuses a Third
By Keane Bhatt | NACLA | April 8, 2013
Thanks to readers’ responses to The New Yorker following my last post, “On Venezuela, The New Yorker’s Jon Lee Anderson Fails at Arithmetic,” the magazine has amended two errors in two separate articles.
The first correction involves an online piece that Anderson wrote on the eve of Venezuela’s elections in October of last year. As was pointed out almost immediately after Anderson’s entry was published, he had incorrectly claimed that “Venezuela leads Latin America in homicides” in his “The End of Chavez?” (the headline was changed to “Chavez the Survivor” after the late Venezuelan president handily won his reelection).
Actually, it is Honduras that leads Latin America—and indeed the entire world—in per capita homicides: 92 per 100,000 people are killed annually there, while Venezuela’s figure stands at 45.1, according to the most recently available United Nations data. And unlike the Venezuelan government, the Honduran government contributes to this body count by regularly murdering its own civilians through its military and police, both of which receive tens of millions of dollars from U.S. taxpayers. (The New Yorker hasn’t published a single article referring to Honduras’s current post-coup regime, headed by Porfirio Lobo, who came to power in January of 2010.)
Reacting to readers’ complaints, the magazine’s editors issued an addendum to Anderson’s October 7 piece, which reads:
*An earlier version of this post said that Venezuela led Latin America in homicides; globally, it was in fourth place, but third in Latin America (behind Honduras and El Salvador), according to U.N. statistics on intentional homicides for 2010-11.
Another Anderson article—“Slumlord: What has Hugo Chávez wrought in Venezuela?”—also misled the print magazine’s readers by giving the impression that Chávez’s presidential tenure was predicated on a coup d’etat rather than his victories in over a dozen internationally vetted elections. The New Yorker released a correction for the inaccuracy in its April 1 issue, two months after the original piece had been published:
In “Slumlord,” by Jon Lee Anderson (January 28th), Hugo Chávez is described as having been concerned with “preventing a coup like the one that put him in office.” In fact, Chávez’s coup attempt, in 1992, failed; he was elected to office in 1998.
For Jon Lee Anderson’s most recent factual error, unfortunately, The New Yorker has thus far refused to issue a clarification or retraction. One month ago—the day Chávez died—Anderson wrote a third piece, for NewYorker.com, claiming:
What [Chávez] has left is a country that, in some ways, will never be the same, and which, in other ways, is the same Venezuela as ever: one of the world’s most oil-rich but socially unequal countries. . .
As I pointed out in “Anderson Fails at Arithmetic,” this allegation misleads the reader in two ways. Inequality has been reduced enormously under Chávez, using its standard measure, the Gini coefficient. So one can hardly say that in this aspect, Venezuela remains the “same as ever.” Making Anderson’s contention even worse is the fact that Venezuela is the most equal country in Latin America, according to the United Nations. Anderson’s readers come away with exactly the opposite impression.
To The New Yorker’s credit, a senior editor sent me an email regarding my article’s criticisms, and flatly conceded the first two misstatements in Anderson’s pieces. However, the note offered a strained defense of Anderson’s position on inequality, arguing that Anderson’s point was valid, given that his claim supposedly combined Venezuela’s conditions of being both “oil-rich” and “socially unequal” as one assertion.
I pointed out in my response that any reasonable reading of the statement would portray Venezuela as both one of the world’s most oil-rich and one of the world’s most socially unequal countries. And the fact of the matter is that the CIA’s World Factbook ranks the country 68th out of 136 countries with available data on income inequality—that is to say, Venezuela is exactly in the middle, and impossible to construe as among the most unequal.
I also explained that when Anderson was confronted with this evidence on Twitter, the magazine’s principal correspondent on Venezuela expressed extreme skepticism toward publicly available, constantly used, and highly scrutinized data; he instead cited his own “reporting” and “impressions” as the authority for his assertions. Given Anderson’s defiant admission not to even pretend to care about empirical data—after his magazine had already retracted two of his articles’ factual claims—it was incumbent on editors and fact-checkers to uphold The New Yorker’s reputation as a trustworthy and evidence-based journal by addressing the issue immediately.
Lastly, I argued that the awkward formulation of combining “oil-rich” and “socially unequal”—a reading I reject—exposes Anderson’s contention as even further at odds with reality. Included in my email was the following list showing the top 10 most “oil-rich” countries ranked in order of their total crude oil production, according to the International Energy Agency. Each country’s corresponding Gini coefficient from the CIA World Factbook appears in parentheses—the higher the Gini coefficient, the greater the country’s inequality:
1. Saudi Arabia (unavailable)
2. Russia (0.42)
3. United States (0.45)
4. Iran (0.445)
5. China (0.48)
6. Canada (0.32)
7. United Arab Emirates (unavailable)
8. Venezuela (0.39)
9. Mexico (0.517)
10. Nigeria (0.437)
When provided with these arguments and data, The New Yorker’s senior editor fell silent in the face of repeated follow-ups. I received a reply only once: a rejection of my request to publicly post our correspondence. While issuing a correction to Anderson’s third Venezuela article over the past year would have been embarrassing, the continued silence and inaction of the elite intellectual journal is perhaps a greater indictment. Anderson’s error remains unchanged on the liberal magazine’s website, while its senior editor has refused to address the matter in private correspondence or offer a public rationale for leaving Anderson’s claim intact.
When asked to comment on this issue, Branko Milanovic—a lead economist at the World Bank and arguably the world’s foremost expert on global inequality—interpreted Anderson’s quote the standard way: “The article says that Venezuela is one of most ‘socially unequal’ countries,” he wrote by email. But The New Yorker’s “extremely vague formulation,” he added, obscured an important reality: “What we know…is that Venezuela is among two or three most equal Latin American countries measured by income inequality.” According to his own research of inequality throughout the world, Venezuela is likely to be ranked somewhere “around the middle, or perhaps slightly above (these things do change from year to year).”
Prominent macroeconomist Dean Baker of the Center for Economic and Policy Research found The New Yorker’s factual contention and subsequent unresponsiveness astonishing: “This is pretty outrageous,” he wrote by email. “Do they have any data to support their assertion, or is the argument that because they don’t like Chávez they can say anything they want about him?”
Readers can pose such questions to The New Yorker by contacting its editors at www.newyorker.com/contact/contactus, by email at tny.newsdesk@gmail.com, or on Twitter at @tnynewsdesk. Such media activism plays a crucial role in engendering more careful portrayals of countries like Venezuela, which has long been the target of cartoonishly hostile, slanted, and outright false media coverage. Previous demands for accuracy and accountability have already prompted two admissions of error by The New Yorker, and can lead to a third, in spite of the magazine’s obstinacy. More importantly, the magazine now faces a real political cost to publishing sloppy reporting, as well as a powerful deterrent to running reckless news and commentary during a politically significant transitional moment for Venezuela.
Related articles
- On Venezuela, The New Yorker’s Jon Lee Anderson Fails at Arithmetic (alethonews.wordpress.com)
- ‘Little Twerp … Get a Life’: The New Yorker’s Jon Lee Anderson Thinks He’s Somebody on Twitter (gawker.com)
“We’re Witnessing a Reactivation of the Death Squads of the ‘80s”
An Interview with Bertha Oliva of COFADEH
By Alex Main | cepr Americas Blog | March 29, 2013
Bertha Oliva is the General Coordinator of COFADEH, the Committee of Relatives of the Disappeared and Detained in Honduras. Bertha’s husband was “disappeared” in 1981, a period when death squads were active in Honduras. She founded COFADEH together with other women who lost their loved ones, in order to seek justice and compensation for the families of the hundreds of dissidents that were “disappeared” between 1979 and 1989. Since then Bertha and COFADEH have taken on some of the country’s most emblematic human rights cases and were a strong voice in opposition to the 2009 coup d’Etat and the repression that followed. We interviewed her in Washington, D.C. on March 15th, shortly after she participated in a hearing on the human rights situation in Honduras at the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights (IACHR). During the hearing she said that death squads are targeting social leaders, lawyers, journalists and other groups and called on the IACHR to visit Honduras in the next six months to take stock of the human rights situation ahead of the November general elections (Bertha’s testimony can be viewed here, beginning at 17:40).
Q: On various occasions you’ve said that what you’re seeing today in Honduras is reminiscent of the difficult times you experienced in the ‘80s and I’d like you to elaborate on that.
In the ‘80s we had armed forces that were excessively empowered. Today Honduras is extremely similar, with military officers exercising control over many of the country’s institutions. The military is now in the streets playing a security role – often substituting for the work of the police forces of the country.
In the ‘80s we also witnessed the practice of forced disappearances and assassinations. In that era it was clear that they were killing social leaders, political opponents, but they also assassinated people who had no ties to dissident groups in order to generate confusion in public opinion and try to disqualify our denunciations of the killings of family members who were political opponents.
Today they assassinate young people in a more atrocious fashion than in the ‘80s and we’re seeing a marked pattern of assassinations of women and youth. And within this mass of people that are assassinated there are political opponents. We refuse to dismiss these assassinations as simply a result of the extreme violence that we’re experiencing, as they try to tell the country. We say that it is a product of impunity and Honduras’ historical debt for failing to resolve cases perpetrated by state agents…
In the ‘80s the presence of the U.S. in the country was extremely significant. Today it’s the same. New bases have opened as a result of an anti-drug cooperation agreement signed between Honduras and the U.S.
In the ‘80s it was clear that political opponents were being eliminated. Today they’re also eliminating those who claim land rights, as exemplified in the Bajo Aguán. More than 98 land rights activists have been assassinated. The campesino sector in the Bajo Aguán has been psychologically and emotionally tortured on top of the physical torture that certain campesino leaders have been subjected to.
Q: Today in the hearing on human rights in Honduras at the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights you discussed death squads. Death squads were active in the ‘80s and now you believe that this sinister phenomenon is coming back.
It’s certain that death squads are a product of the impunity that we’ve seen in Honduras. The death squads of the past were never really dismantled. What we’re witnessing is a reactivation of these death squads. And we’re seeing it quite clearly. We’ve seen videos of incidents in the street where masked men with military training and unmarked vehicles assassinate young people. There is the recent case of the journalist Julio Ernesto Alvarado who gave up his news program from 10pm to midnight on Radio Globo because members of a death squad came to kill him, and to save his own life he had to stop doing his program.
In Honduras we had a military coup d’Etat and this resulted in persecution, an implosion of the state’s institutions which has left us with a dysfunctional judicial system and this has provided cover to those who wish to break the law.
And, what’s worse, state agents seem to have no political interest in improving and changing the situation. What we’re witnessing is a growing professionalization of the capacity to justify illegal acts: authorities’ assertion that they intend to investigate these acts, when that’s simply not true. In reality it seems the intention is to continue terrorizing the Honduran people, to make them submissive so as to undermine citizen action.
What we’d like to see in Honduras is real action to try to prevent crime rather than continued justification of the lack of progress of investigations into crimes.
Q: COFADEH is providing legal counsel to the victims and the families of the victims of the emblematic case that took place in May of last year in Ahuas, in which there was a police operation that involved U.S. agents and Honduran security agents that killed four people and injured a few others. Can you discuss the status of that case, over ten months after the killings took place?
Yes, we are the legal representatives of the victims in this case and, on the one hand, we are filing a complaint with Honduras’ judicial authorities to show or verify the responsibility of Honduran agents and DEA agents that participated in this incident.
But we’re also trying to reach out to the general public so that the case is better known and debated as this is the only real recourse we human rights defenders have: publicly denouncing the incident to see whether this will allow for some protection of the victims and of ourselves. But legally we see this as a very difficult case to move forward and this is where we can see that the authorities aren’t interested in investigating, let alone sanctioning, those responsible. The crime of the tragic attack against this indigenous community has been compounded by the crime of violating due process in the investigation.
We the legal representatives of the victims should have access to the case file. The Public Ministry [equivalent to the Attorney General’s Office in the U.S. – ed.] shouldn’t allow any obstacle to come in the way of our access to the file. They can’t legally prevent us from learning about the actions that have been taken in the course of the investigation because we are part of the defense. It is prohibited for either of the parties to be denied access to the case file. The file can be classified with regard to the general public, but not with regard to the parties representing the victims and the accused.
We haven’t seen all the files in this case. They haven’t been inserted in a binder [as is normally the case] in order to allow them to remove information when we ask for the file. How can we participate effectively in a trial when we can’t see all of the case file?
Q: And what evidence do you have of their having removed parts of the case file before sharing it with you?
One is that when we’ve been shown the case file it basically only contains documents that we’ve produced. We know the Public Ministry has carried out its own investigations; it has carried out the exhumation and autopsies of the deceased victims’ bodies for instance. As a side note, we weren’t informed that they were carrying out the exhumations of the victims. We’re left with the impression that the intention isn’t to find evidence but rather to remove [borrar] evidence… Our Public Ministry should be called a “Public Laundromat” because they’re engaged in destroying evidence.
Q: So you didn’t see the reports on the exhumations and autopsies of the victims in the Ahuas case file?
We haven’t seen them, just as we didn’t see the report that was sent by [Honduran Attorney General equivalent] Luís Alberto Rubi to the State Department of the United States. This indicates to us that they remove information and documentation from the case file that they don’t want us to see.
The Public Prosecutor [Attorney General equivalent] sent a report to a representative of the State Department, Maria Otero, with – for instance – the names of the Honduran police agents and military personnel that participated in the operation, though not the names of the DEA agents, with the apparent goal of barring them from any sort of responsibility.
Q: But you did end up managing to see the Public Ministry report sent to the State Department?
Yes, but not through the Public Ministry, but thanks to people outside Honduras who managed to get hold of a copy.
Q: In this report there is information based on testimony provided to the Public Ministry by police agents that participated in the Ahuas operation. Have you been able to see any of this original testimony?
No, we haven’t seen any of the testimony of the police agents.
Q: What is the current situation of the surviving victims of the Ahuas incident, and of the families of the victims?
The situation of the families, of the survivors, of the community is really very critical. They are emotionally and psychologically affected. Being on the receiving end of an armed aerial attack is a shock for a remote community that never expected an attack of this nature. Some of the community members were woken up by armed agents, were physically attacked and had certain belongings stolen.
I think that those that survived are no longer directly threatened but not all of them have recovered their physical abilities. For instance, a young man sustained a serious injury to his hand requiring an operation that cost 100,000 lempiras [over $5,000 – ed.]. Where can this boy, who doesn’t have anything, find this kind of money?
COFADEH ended up having to take care of him and he’s still in treatment in Tegucigalpa, far from his community. We are paying for his treatment and lodging him, feeding him and paying for his studies. This is the responsibility of the state and it has refused to assume this responsibility even though we requested urgent protective measures from the state. The state is good at providing technically well-designed reports before the Inter-American Commission on Human Rights, but it has been incapable of dealing with the needs of the survivors of this attack.
This sort of thing is a clear demonstration of their lack of interest in resolving and combatting the insecurity we’re experiencing, the political violence and the high level of impunity.
Q: What about the other injured victims?
We’ve had to bring them to Tegucigalpa to be treated. In the case of one boy they left studs [clavos] jutting out of his arm. He almost lost his arm because after the operation they sent him back to his community but with no medicine.
We’ve also had to provide care for other relatives of the survivors and the deceased victims. It’s impressive the level of neglect of these victims on the part of the state.
We [the human rights defenders] return to our country with the fear that the attacks will extend to us as a result of our decision to come and denounce a state that has shown itself incapable of assuming its responsibility.
Q: COFADEH has received threats and recently its offices were raided. Can you talk to me about your situation, your vulnerability, and what people in the U.S. can do to help?
Our situation isn’t good at all. I confess that we’re frightened because we love life, that’s why we dedicate ourselves to defending the lives of others. And I don’t want to die or be tortured. And I don’t want to have to confront state agents. But despite their machinery of hate and actions against us, they should know that they can’t stop us.
Fortunately we can count on support from people in the U.S. and the rest of the world, and I can reaffirm today that this support and this commitment of people abroad inspires us and makes us feel less alone. Because the worst that can happen for a human rights defender facing threats is to feel alone. That’s why we call on you to continue supporting us to defend the life and liberty of the citizens that need our help.
Related articles
- World Bank Must End Support for Honduran Palm Oil Company Implicated in Murder (alethonews.wordpress.com)
- Will Congress act to stop US support for Honduras’ death squad regime? | Mark Weisbrot (guardian.co.uk)